Transcripts targeted by the microRNA-16 family cooperatively regulate cell cycle progression
- PMID: 17242205
- PMCID: PMC1820501
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02005-06
Transcripts targeted by the microRNA-16 family cooperatively regulate cell cycle progression
Abstract
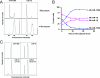
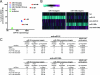
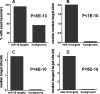
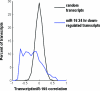
microRNAs (miRNAs) are abundant, approximately 21-nucleotide, noncoding regulatory RNAs. Each miRNA may regulate hundreds of mRNA targets, but the identities of these targets and the processes they regulate are poorly understood. Here we have explored the use of microarray profiling and functional screening to identify targets and biological processes triggered by the transfection of human cells with miRNAs. We demonstrate that a family of miRNAs sharing sequence identity with miRNA-16 (miR-16) negatively regulates cellular growth and cell cycle progression. miR-16-down-regulated transcripts were enriched with genes whose silencing by small interfering RNAs causes an accumulation of cells in G(0)/G(1). Simultaneous silencing of these genes was more effective at blocking cell cycle progression than disruption of the individual genes. Thus, miR-16 coordinately regulates targets that may act in concert to control cell cycle progression.
Figures


References
-
- Ambros, V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431:350-355. - PubMed
-
- Bagga, S., J. Bracht, S. Hunter, K. Massirer, J. Holtz, R. Eachus, and A. E. Pasquinelli. 2005. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell 122:553-563. - PubMed
-
- Bartel, D. P., and C. Z. Chen. 2004. Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 5:396-400. - PubMed
-
- Bentwich, I. 2005. Prediction and validation of microRNAs and their targets. FEBS Lett. 579:5904-5910. - PubMed
-
- Bentwich, I., A. Avniel, Y. Karov, R. Aharonov, S. Gilad, O. Barad, A. Barzilai, P. Einat, U. Einav, E. Meiri, E. Sharon, Y. Spector, and Z. Bentwich. 2005. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat. Genet. 37:766-770. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
