Subcellular transport of EKLF and switch-on of murine adult beta maj globin gene transcription
- PMID: 17242208
- PMCID: PMC1820495
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01875-06
Subcellular transport of EKLF and switch-on of murine adult beta maj globin gene transcription
Abstract
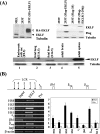
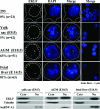
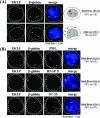
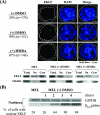
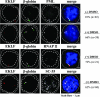
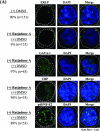
Erythroid Krüppel-like factor (EKLF) is an essential transcription factor for mammalian beta-like globin gene switching, and it specifically activates transcription of the adult beta globin gene through binding of its zinc fingers to the promoter. It has been a puzzle that in the mouse, despite its expression throughout the erythroid development, EKLF activates the adult beta(maj) globin promoter only in erythroid cells beyond the stage of embryonic day 10.5 (E10.5) but not before. We show here that expression of the mouse beta(maj) globin gene in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region of E10.5 embryos and in the E14.5 fetal liver is accompanied by predominantly nuclear localization of EKLF. In contrast, EKLF is mainly cytoplasmic in the erythroid cells of E9.5 blood islands in which beta(maj) is silenced. Remarkably, in a cultured mouse adult erythroleukemic (MEL) cell line, the activation of the beta(maj) globin gene by dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or hexamethylene-bis-acetamide (HMBA) induction is also paralleled by a shift of the subcellular location of EKLF from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. Blockage of the nuclear import of EKLF in DMSO-induced MEL cells with a nuclear export inhibitor repressed the transcription of the beta(maj) globin gene. Transient transfection experiments further indicated that the full-sequence context of EKLF was required for the regulation of its subcellular locations in MEL cells during DMSO induction. Finally, in both the E14.5 fetal liver cells and induced MEL cells, the beta-like globin locus is colocalized the PML oncogene domain nuclear body, and concentrated with EKLF, RNA polymerase II, and the splicing factor SC35. These data together provide the first evidence that developmental stage- and differentiation state-specific regulation of the nuclear transport of EKLF might be one of the steps necessary for the switch-on of the mammalian adult beta globin gene transcription.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Chromatin-binding in vivo of the erythroid kruppel-like factor, EKLF, in the murine globin loci.Cell Res. 2006 Apr;16(4):347-55. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7310045. Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16617330
-
Erythroid Krüppel-like factor (EKLF) is active in primitive and definitive erythroid cells and is required for the function of 5'HS3 of the beta-globin locus control region.EMBO J. 1998 Apr 15;17(8):2334-41. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.8.2334. EMBO J. 1998. PMID: 9545245 Free PMC article.
-
Major erythrocyte membrane protein genes in EKLF-deficient mice.Exp Hematol. 2006 Jun;34(6):705-12. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2006.02.018. Exp Hematol. 2006. PMID: 16728274
-
Transcriptional factors for specific globin genes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Jun 30;850:64-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb10463.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9668528 Review.
-
Can mutations in the gene encoding transcription factor EKLF (Erythroid Krüppel-Like Factor) protect us against infectious and parasitic diseases?Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016 Oct 6;70(0):1068-1086. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1221384. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016. PMID: 27708211 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional interactions between erythroid Krüppel-like factor (EKLF/KLF1) and protein phosphatase PPM1B/PP2Cβ.J Biol Chem. 2012 May 4;287(19):15193-204. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.350496. Epub 2012 Mar 5. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22393050 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular dynamics of mammalian red blood cell production in the erythroblastic island niche.Biophys Rev. 2019 Dec;11(6):873-894. doi: 10.1007/s12551-019-00579-2. Epub 2019 Aug 15. Biophys Rev. 2019. PMID: 31418139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KLF1/EKLF expression in acute leukemia is correlated with chromosomal abnormalities.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020 Jul;83:102434. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2020.102434. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2020. PMID: 32311573 Free PMC article.
-
EKLF/KLF1, a tissue-restricted integrator of transcriptional control, chromatin remodeling, and lineage determination.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;33(1):4-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01058-12. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23090966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative splicing of EKLF/KLF1 in murine primary erythroid tissues.Exp Hematol. 2015 Jan;43(1):65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2014.08.007. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Exp Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25283745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baron, M. H. 2003. Embryonic origins of mammalian hematopoiesis. Exp. Hematol. 31:1160-1169. - PubMed
-
- Bieker, J. J. 2005. Probing the onset and regulation of erythroid cell-specific gene expression. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 72:333-338. - PubMed
-
- Bulger, M., and M. Groudine. 1999. Looping versus linking: toward a model for long-distance gene activation. Genes Dev. 13:2465-2477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
