Interleukin-6 impairs the insulin signaling pathway, promoting production of nitric oxide in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- PMID: 17242212
- PMCID: PMC1820492
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01340-06
Interleukin-6 impairs the insulin signaling pathway, promoting production of nitric oxide in human umbilical vein endothelial cells
Abstract
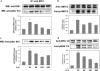
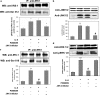
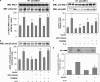
Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an independent predictor of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease and is correlated with insulin resistance. Insulin stimulates nitric oxide (NO) production through the IRS-1/PI3-kinase/Akt/eNOS pathway (where IRS-1 is insulin receptor substrate 1, PI3-kinase is phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and eNOS is endothelial NO synthase). We asked if IL-6 affects insulin vasodilator action both in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and in the aortas of C57BL/6J mice and whether this inhibitory effect was caused by increased Ser phosphorylation of IRS-1. We observed that IL-6 increased IRS-1 phosphorylation at Ser(312) and Ser(616); these effects were paralleled by increased Jun N-terminal protein kinase (JNK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation and reversed by JNK and ERK1/2 inhibition. In addition, IL-6 treatment resulted in impaired IRS-1 phosphorylation at Tyr(612), a site essential for engaging PI3-kinase. Furthermore, IL-6 treatment reduced insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of eNOS at the stimulatory Ser(1177) site and impaired insulin-stimulated eNOS dephosphorylation at the inhibitory Thr(495) site. Insulin-stimulated eNOS activation and NO production were also inhibited by IL-6; these effects were reversed by inhibition of JNK and ERK1/2. Treatment of C57BL/6J mice with IL-6 resulted in impaired insulin-dependent activation of the Akt/eNOS pathway in the aorta as a result of JNK and ERK1/2 activation. Our data suggest that IL-6 impairs the vasodilator effects of insulin that are mediated by the IRS-1/PI3-kinase/Akt/eNOS pathway through activation of JNK and ERK1/2.
Figures



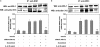



References
-
- Aguirre, V., T. Uchida, L. Yenush, R. Davis, and M. F. White. 2000. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J. Biol. Chem. 275:9047-9054. - PubMed
-
- Andreozzi, F., E. Laratta, A. Sciacqua, F. Perticone, and G. Sesti. 2004. Angiotensin II impairs the insulin signalling pathway promoting production of nitric oxide by inducing phosphorylation of IRS-1 on Ser312 and Ser616 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 94:1211-1218. - PubMed
-
- Balletshofer, B. M., K. Rittig, M. D Enderle, et al. 2000. Endothelial dysfunction is detectable in young normotensive first-degree relatives of subjects with type 2 diabetes in association with insulin resistance. Circulation 101:1780-1784. - PubMed
-
- De Fea, K., and R. A. Roth. 1997. Modulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 tyrosine phosphorylation and function by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 272:31400-31406. - PubMed
-
- De Fea, K., and R. A. Roth. 1997. Protein kinase C modulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 tyrosine phosphorylation requires serine 612. Biochemistry 36:12939-12947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
