Large-scale phosphorylation analysis of mouse liver
- PMID: 17242355
- PMCID: PMC1785252
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609836104
Large-scale phosphorylation analysis of mouse liver
Abstract
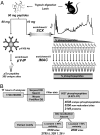
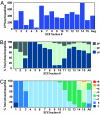
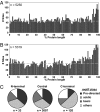
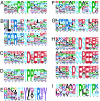
Protein phosphorylation is a complex network of signaling and regulatory events that affects virtually every cellular process. Our understanding of the nature of this network as a whole remains limited, largely because of an array of technical challenges in the isolation and high-throughput sequencing of phosphorylated species. In the present work, we demonstrate that a combination of tandem phosphopeptide enrichment methods, high performance MS, and optimized database search/data filtering strategies is a powerful tool for surveying the phosphoproteome. Using our integrated analytical platform, we report the identification of 5,635 nonredundant phosphorylation sites from 2,328 proteins from mouse liver. From this list of sites, we extracted both novel and known motifs for specific Ser/Thr kinases including a "dipolar" motif. We also found that C-terminal phosphorylation was more frequent than at any other location and that the distribution of potential kinases for these sites was unique. Finally, we identified double phosphorylation motifs that may be involved in ordered phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hunter T. Cell. 2000;100:113–127. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T, Scott JD. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:286–290. - PubMed
-
- Manning G, Whyte DB, Martinez R, Hunter T, Sudarsanam S. Science. 2002;298:1912–1934. - PubMed
-
- Songyang Z, Blechner S, Hoagland N, Hoekstra MF, Piwnica-Worms H, Cantley LC. Curr Biol. 1994;4:973–982. - PubMed
-
- Hutti JE, Jarrell ET, Chang JD, Abbott DW, Storz P, Toker A, Cantley LC, Turk BE. Nat Methods. 2004;1:27–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

