Histopathological study of time course changes in inter-renal aortic banding-induced left ventricular hypertrophy of mice
- PMID: 17244336
- PMCID: PMC2517284
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2006.00514.x
Histopathological study of time course changes in inter-renal aortic banding-induced left ventricular hypertrophy of mice
Abstract
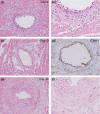
The left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) in response to pressure overload is an important risk factor in cardiac morbidity and mortality. To investigate the time course of histopathological alterations in the LVH in response to pressure overload, histopathological and immunohistochemical examination was performed using the aortic banding-induced mouse LVH model. Five-week-old male CD-1 mice were subjected to the inter-renal aortic banding. Major organs were sampled on 3, 10, 14, 21, 28 or 42 days after banding. Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, Masson's trichrome staining and immunohistochemistry for proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), alpha-smooth muscle actin (aSMA), ICAM-1, type I collagen and CD31 was performed and microscopically examined. Three days after aortic banding, acute inflammatory changes, such as macrophages/neutrophil infiltration and vascular wall injury were observed on/around the coronary arteries/arterioles of both ventricles. Intense ICAM-1 immunostaining was observed on the endothelium of the coronary arteries/arterioles. After day 10, vascular wall thickening and perivascular fibrosis was induced on the coronary arteries/arterioles. Immunohistochemistry for aSMA and PCNA demonstrated the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells in the media. After day 28, minimal cardiomyocyte hypertrophy was observed at the light microscope level. In the inter-renal aortic banding LVH model, histopathological alterations in early phase were mainly observed on coronary arteries/arterioles. These early phase alterations were thought to be hypertension-related changes in the coronary vasculatures. The cardiomyocyte hypertrophy observed in later phase was minimal at the light microscope level. These evidences would facilitate the understanding of pathophysiology of pressure overload LVH.
Figures



References
-
- Baker KM, Chernin MI, Wixson SK, Aceto JF. Renin-angiotensin system involvement in pressure-overload cardiac hypertrophy in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1990;259:H324–H332. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa ME, Alenina N, Bader M. Induction and analysis of cardiac hypertrophy in transgenic animal models. Methods Mol. Med. 2005;112:339–352. - PubMed
-
- Brede M, Wiesmann F, Jahns R, et al. Feedback inhibition of catecholamine release by two different alpha2-adrenoceptor subtypes prevents progression of heart failure. Circulation. 2002;106:2491–2496. - PubMed
-
- Brilla CG, Janicki JS, Weber KT. Impaired diastolic function and coronary reserve in genetic hypertension. Role of interstitial fibrosis and medial thickening of intramyocardial coronary arteries. Circ. Res. 1991;69:107–115. - PubMed
-
- Donath MY, Zierhut W, Gosteli-Peter MA, Hauri C, Froesch ER, Zapf J. Effects of IGF-I on cardiac growth and expression of mRNAs coding for cardiac proteins after induction of heart hypertrophy in the rat. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1998;139:109–117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

