Interleukin-1-induced NF-kappaB activation is NEMO-dependent but does not require IKKbeta
- PMID: 17244613
- PMCID: PMC2824644
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M609613200
Interleukin-1-induced NF-kappaB activation is NEMO-dependent but does not require IKKbeta
Abstract
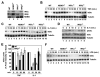
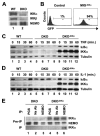
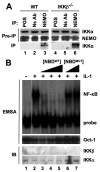
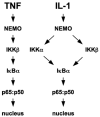
Activation of NF-kappaB by the pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1 (IL-1) requires the IkappaB kinase (IKK) complex, which contains two kinases named IKKalpha and IKKbeta and a critical regulatory subunit named NEMO. Although we have previously demonstrated that NEMO associates with both IKKs, genetic studies reveal that only its interaction with IKKbeta is required for TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation. To determine whether NEMO and IKKalpha can form a functional IKK complex capable of activating the classical NF-kappaB pathway in the absence of IKKbeta, we utilized a panel of mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) lacking each of the IKK complex subunits. This confirmed that TNF-induced IkappaBalpha degradation absolutely requires NEMO and IKKbeta. In contrast, we consistently observed intact IkappaBalpha degradation and NF-kappaB activation in response to IL-1 in two separate cell lines lacking IKKbeta. Furthermore, exogenously expressed, catalytically inactive IKKbeta blocked TNF- but not IL-1-induced IkappaBalpha degradation in wild-type MEFs, and reconstitution of IKKalpha/beta double knockout cells with IKKalpha rescued IL-1- but not TNF-induced NF-kappaB activation. Finally, we have shown that incubation of IKKbeta-deficient MEFs with a cell-permeable peptide that blocks the interaction of NEMO with the IKKs inhibits IL-1-induced NF-kappaB activation. Our results therefore demonstrate that NEMO and IKKalpha can form a functional IKK complex that activates the classical NF-kappaB pathway in response to IL-1 but not TNF. These findings further suggest NEMO differentially regulates the fidelity of the IKK subunits activated by distinct upstream signaling pathways.
Figures



References
-
- Bonizzi G, Karin M. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:280–288. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Genes Dev. 2004;18:2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621–663. - PubMed
-
- May MJ, Larsen SE, Shim JH, Madge LA, Ghosh S. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:45528–45539. - PubMed
-
- May MJ, D'Acquisto F, Madge LA, Glockner J, Pober JS, Ghosh S. Science. 2000;289:1550–1554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

