Pharmacological characterization of mouse GPRC6A, an L-alpha-amino-acid receptor modulated by divalent cations
- PMID: 17245368
- PMCID: PMC2013871
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707121
Pharmacological characterization of mouse GPRC6A, an L-alpha-amino-acid receptor modulated by divalent cations
Abstract
Background and purpose: GPRC6A is a novel member of family C of G protein-coupled receptors with so far unknown function. We have recently described both human and mouse GPRC6A as receptors for L-alpha-amino acids. To date, functional characterization of wild-type GPRC6A has been impaired by the lack of activity in quantitative functional assays. The aim of this study was thus to develop such an assay and extend the pharmacological characterization of GPRC6A.
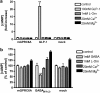
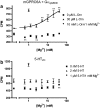
Experimental approach: We have engineered a novel cell-based inositol phosphate turnover assay for wild-type mouse GPRC6A based on transient co-expression with the promiscuous Galpha(qG66D) protein, known to increase receptor signalling sensitivity. This assay allowed for measurements of L-alpha-amino acid potencies. Furthermore, in combination with an assay measuring inward currents at Ca(2+)-activated chloride channels in Xenopus oocytes, the divalent cation-sensing ability of the receptor was examined.
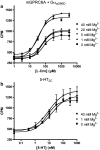
Key results: Using our novel assay, we demonstrate that the basic L-alpha-amino acids ornithine, lysine, and arginine are the most potent agonists at wild-type mouse GPRC6A. Using two different assay systems, we show that divalent cations do not activate the G(q) signalling pathway of mouse GPRC6A per se but positively modulate the amino-acid response.
Conclusions and implications: This is the first reported assay for a wild-type GPRC6A successfully applied for quantitative pharmacological characterization of amino acid and divalent cation responses at mouse GPRC6A. The assay enables further search for GPRC6A ligands such as allosteric modulators, which may provide essential information about the physiological function of GPRC6A.
Figures
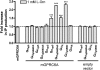

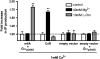
Similar articles
-
The GPCR, class C, group 6, subtype A (GPRC6A) receptor: from cloning to physiological function.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Mar;171(5):1129-41. doi: 10.1111/bph.12365. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24032653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The rat GPRC6A: cloning and characterization.Gene. 2007 Jul 15;396(2):257-67. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2007.03.008. Epub 2007 Mar 24. Gene. 2007. PMID: 17478059
-
Molecular determinants of non-competitive antagonist binding to the mouse GPRC6A receptor.Cell Calcium. 2009 Nov-Dec;46(5-6):323-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2009.09.004. Cell Calcium. 2009. PMID: 19836834
-
Cloning and characterization of a family C orphan G-protein coupled receptor.J Neurochem. 2005 Apr;93(2):383-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03025.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15816861
-
Techniques: promiscuous Galpha proteins in basic research and drug discovery.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Nov;26(11):595-602. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2005.09.007. Epub 2005 Sep 23. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16183138 Review.
Cited by
-
The unique role of dietary L-arginine in the acceleration of peritoneal macrophage sensitivity to bacterial endotoxin.Immunol Res. 2013 May;56(1):73-84. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8379-2. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 23184235
-
Luminal Chemosensory Cells in the Small Intestine.Nutrients. 2021 Oct 22;13(11):3712. doi: 10.3390/nu13113712. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34835968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The GPCR, class C, group 6, subtype A (GPRC6A) receptor: from cloning to physiological function.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Mar;171(5):1129-41. doi: 10.1111/bph.12365. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24032653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of N-benzyl phenethylamines as 5-HT2A/2C agonists.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Mar 19;5(3):243-9. doi: 10.1021/cn400216u. Epub 2014 Jan 15. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24397362 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric modulation of the calcium-sensing receptor.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2007 Sep;5(3):180-6. doi: 10.2174/157015907781695982. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2007. PMID: 19305800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brandish PE, Hill LA, Zheng W, Scolnick EM. Scintillation proximity assay of inositol phosphates in cell extracts: high-throughput measurement of G-protein-coupled receptor activation. Anal Biochem. 2003;313:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M, Butters R, Kifor O, et al. Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature. 1993;366:575–580. - PubMed
-
- Chahine M, Bennett PB, George AL, Jr, Horn R. Functional expression and properties of the human skeletal muscle sodium channel. Pflügers Arch. 1994;427:136–142. - PubMed
-
- Conklin BR, Farfel Z, Lustig KD, Julius D, Bourne HR. Substitution of three amino acids switches receptor specificity of Gqα to that of Giα. Nature. 1993;363:274–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

