Cancer chemopreventive properties of orally bioavailable flavonoids--methylated versus unmethylated flavones
- PMID: 17250812
- PMCID: PMC1868573
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.12.028
Cancer chemopreventive properties of orally bioavailable flavonoids--methylated versus unmethylated flavones
Abstract
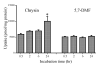
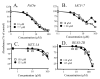
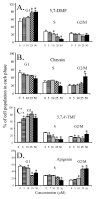
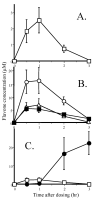
Poor oral bioavailability has been a major limitation for the successful use of dietary flavonoids as cancer chemopreventive agents. In this study, we examined fully methylated flavones as promising improved agents. In the human oral SCC-9 cancer cells, 5,7-dimethoxyflavone and 5,7,4'-trimethoxyflavone were both 10 times more potent inhibitors of cell proliferation (IC(50) values 5-8 microM) than the corresponding unmethylated analogs chrysin and apigenin. Flow cytometry indicated that both methylated flavones arrested the SCC-9 cells in the G1 phase with a concomitant decrease in the S phase, dramatically different from the unmethylated analogs, which promoted G2/M phase arrest. Both methylated compounds inhibited the proliferation of two other cancer cell lines with very little effect on two immortalized normal cell lines. Examination of additional flavone structures indicated that methylated flavones in general have antiproliferative properties. Finally, we demonstrated that 5,7-dimethoxyflavone, in contrast to its unmethylated analog chrysin, was well absorbed and had high oral bioavailability as well as tissue accumulation in vivo in the rat. Thus, fully methylated flavones appear to have great potential as cancer chemopreventive/chemotherapeutic agents, in particular in oral cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Middleton EJ, Kandaswami C, Theoharides TC. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:673–751. - PubMed
-
- Yang CS, Prabhu S, Landau J. Prevention of carcinogenesis by tea polyphenols. Drug Metab Rev. 2001;33:237–53. - PubMed
-
- Pervaiz S. Resveratrol: from grapevines to mammalian biology. FASEB J. 2003;17:1975–85. - PubMed
-
- Haghiac M, Walle T. Quercetin induces necrosis and apoptosis in the SCC-9 oral cancer cells. Nutr Cancer. 2005;53:220–31. - PubMed
-
- Fang J, Xia C, Cao Z, Zheng JZ, Reed E, Jiang B-H. Apigenin inhibits VEGF and HIF-1 expression via PI3K/AKT/p70S6K1 and HDM2/p53 pathways. FASEB J. 2005;19:342–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

