Structure-dependent functional properties of human defensin 5
- PMID: 17250830
- PMCID: PMC1832120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.12.036
Structure-dependent functional properties of human defensin 5
Abstract
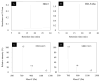
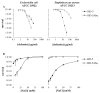
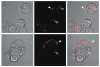
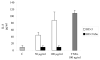
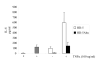
The mucosal epithelium secretes a variety of antimicrobial peptides that act as part of the innate immune system to protect against invading microbes. Here, we describe the functional properties of human defensin (HD) 5, the major antimicrobial peptide produced by Paneth cells in the ileum, in relation to its structure. The antimicrobial activity of HD-5 against Escherichia coli proved to be independent of its structure, whereas the unstructured peptide showed greatly reduced antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus. We find that HD-5 binds to the cell membrane of intestinal epithelial cells and induced secretion of the chemokine interleukin (IL)-8 in a concentration- and structure-dependent fashion. Incubation of HD-5 in the presence of tumor necrosis factor alpha further increased IL-8 secretion synergistically, suggesting that HD-5 may act as a regulator of the intestinal inflammatory response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional synergism of Human Defensin 5 and Human Defensin 6.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Nov 27;467(4):967-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.10.035. Epub 2015 Oct 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26474700
-
Alpha-defensins in the gastrointestinal tract.Mol Immunol. 2003 Nov;40(7):463-7. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(03)00157-3. Mol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14568393 Review.
-
Precursor processing of human defensin-5 is essential to the multiple functions in vitro and in vivo.J Innate Immun. 2010;2(1):66-76. doi: 10.1159/000242114. Epub 2009 Sep 22. J Innate Immun. 2010. PMID: 20375624
-
Paneth cell alpha-defensins: peptide mediators of innate immunity in the small intestine.Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2005 Sep;27(2):133-46. doi: 10.1007/s00281-005-0202-x. Epub 2005 Jun 2. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2005. PMID: 15931529 Review.
-
Paneth cell α-defensin 6 (HD-6) is an antimicrobial peptide.Mucosal Immunol. 2015 May;8(3):661-71. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.100. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Mucosal Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25354318 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A novel horse alpha-defensin: gene transcription, recombinant expression and characterization of the structure and function.Biochem J. 2007 Oct 15;407(2):267-76. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070747. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17620056 Free PMC article.
-
NMR solution structure and condition-dependent oligomerization of the antimicrobial peptide human defensin 5.Biochemistry. 2012 Dec 4;51(48):9624-37. doi: 10.1021/bi301255u. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Biochemistry. 2012. PMID: 23163963 Free PMC article.
-
Trp-26 imparts functional versatility to human alpha-defensin HNP1.J Biol Chem. 2010 May 21;285(21):16275-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102749. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20220136 Free PMC article.
-
The conserved salt bridge in human alpha-defensin 5 is required for its precursor processing and proteolytic stability.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 1;283(31):21509-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801851200. Epub 2008 May 22. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18499668 Free PMC article.
-
Nanodefensin-encased hydrogel with dual bactericidal and pro-regenerative functions for advanced wound therapy.Theranostics. 2021 Jan 26;11(8):3642-3660. doi: 10.7150/thno.53089. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33664853 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

