Proteins from extremophiles as stable tools for advanced biotechnological applications of high social interest
- PMID: 17251151
- PMCID: PMC2359841
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2006.0174
Proteins from extremophiles as stable tools for advanced biotechnological applications of high social interest
Abstract
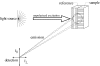
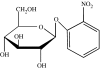
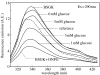
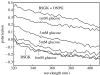
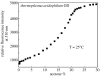
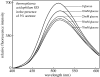
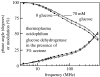
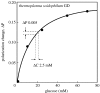
Extremophiles are micro-organisms adapted to survive in ecological niches defined as 'extreme' for humans and characterized by the presence of adverse environmental conditions, such as high or low temperatures, extreme values of pH, high salt concentrations or high pressure. Biomolecules isolated from extremophiles possess extraordinary properties and, in particular, proteins isolated from extremophiles represent unique biomolecules that function under severe conditions, comparable to those prevailing in various industrial processes. In this article, we will review some examples of recent applications of thermophilic proteins for the development of a new class of fluorescence non-consuming substrate biosensors for monitoring the levels of two analytes of high social interest, such as glucose and sodium.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protein-based biosensors for diabetic patients.J Fluoresc. 2004 Sep;14(5):491-8. doi: 10.1023/b:jofl.0000039337.30726.6d. J Fluoresc. 2004. PMID: 15617257
-
Protein adaptations in archaeal extremophiles.Archaea. 2013;2013:373275. doi: 10.1155/2013/373275. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Archaea. 2013. PMID: 24151449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extremophiles as a source of novel enzymes for industrial application.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999 Jun;51(6):711-29. doi: 10.1007/s002530051456. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999. PMID: 10422220 Review.
-
A novel fluorescence competitive assay for glucose determinations by using a thermostable glucokinase from the thermophilic microorganism Bacillus stearothermophilus.Anal Biochem. 2002 Apr 15;303(2):138-44. doi: 10.1006/abio.2001.5544. Anal Biochem. 2002. PMID: 11950213 Free PMC article.
-
Marine extremophiles: a source of hydrolases for biotechnological applications.Mar Drugs. 2015 Apr 3;13(4):1925-65. doi: 10.3390/md13041925. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25854643 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the enigmatic PilY1 of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans: An in silico analysis.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Jul 26;39:101797. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101797. eCollection 2024 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39161578 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the biomass hydrolysis potential in bacterial isolates from a volcanic environment: biosynthesis of the corresponding activities.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Sep;28(9):2889-902. doi: 10.1007/s11274-012-1100-8. Epub 2012 Jun 20. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22806730
-
Addressing the Selectivity of Enzyme Biosensors: Solutions and Perspectives.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Apr 26;21(9):3038. doi: 10.3390/s21093038. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33926034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Enzymes From the Red Sea Brine Pools: Current State and Potential.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 27;12:732856. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.732856. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34777282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring microbial diversity in the Kharasinpur hot spring of West Bengal, India.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 17;52(1):608. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10690-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40528093
References
-
- Amato I. In search of the human touch. Science. 1992;258, 5087:1436–1437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

