Polarization of hippocampal neurons with competitive surface stimuli: contact guidance cues are preferred over chemical ligands
- PMID: 17251152
- PMCID: PMC2359858
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2006.0171
Polarization of hippocampal neurons with competitive surface stimuli: contact guidance cues are preferred over chemical ligands
Abstract
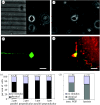
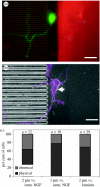
Neuronal behaviour is profoundly influenced by extracellular stimuli in many developmental and regeneration processes. Understanding neuron responses and integration of environmental signals could impact the design of successful therapies for neurodegenerative diseases and nerve injuries. Here, we have investigated the influence of localized extracellular cues on polarization (i.e. axon formation) of hippocampal neurons. Electron-beam lithography, microfabrication techniques and protein immobilization were used to create a unique system that provided simultaneous and independent chemical and physical cues to individual neurons. In particular, we analysed competitive responses between simultaneous stimulation with chemical ligands, including immobilized nerve growth factor and laminin, and contact guidance cues mediated by surface topography (i.e. microchannels). Contact guidance cues were preferred 70% of the time over chemical ligands by neurons extending axons, which suggests a stronger stimulation mechanism triggered by topography. This investigation contributes to the understanding of neuronal behaviour on artificial substrates, which is applicable to the creation of artificial environments for neural engineering applications.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Immobilized nerve growth factor and microtopography have distinct effects on polarization versus axon elongation in hippocampal cells in culture.Biomaterials. 2007 Jan;28(2):271-84. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.07.043. Epub 2006 Aug 17. Biomaterials. 2007. PMID: 16919328
-
Local presentation of substrate molecules directs axon specification by cultured hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 1999 Aug 1;19(15):6417-26. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-15-06417.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10414970 Free PMC article.
-
Computational model provides insight into the distinct responses of neurons to chemical and topographical cues.Ann Biomed Eng. 2009 Feb;37(2):363-74. doi: 10.1007/s10439-008-9613-x. Epub 2008 Dec 9. Ann Biomed Eng. 2009. PMID: 19067167 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in membrane trafficking and actin dynamics during axon formation in cultured hippocampal neurons.Microsc Res Tech. 2000 Jan 1;48(1):3-11. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0029(20000101)48:1<3::AID-JEMT2>3.0.CO;2-O. Microsc Res Tech. 2000. PMID: 10620780 Review.
-
Neuronal polarization.Development. 2015 Jun 15;142(12):2088-93. doi: 10.1242/dev.114454. Development. 2015. PMID: 26081570 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective axonal growth of embryonic hippocampal neurons according to topographic features of various sizes and shapes.Int J Nanomedicine. 2010 Dec 22;6:45-57. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S12376. Int J Nanomedicine. 2010. PMID: 21289981 Free PMC article.
-
Microelectrode array-induced neuronal alignment directs neurite outgrowth: analysis using a fast Fourier transform (FFT).Eur Biophys J. 2017 Dec;46(8):719-727. doi: 10.1007/s00249-017-1263-1. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Eur Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 29075798
-
Recent advances in nanotherapeutic strategies for spinal cord injury repair.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019 Aug;148:38-59. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2018.12.011. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019. PMID: 30582938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and Subcellular Contact Guidance on Microfabricated Substrates.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020 Oct 22;8:551505. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.551505. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33195116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Polarity in Cerebral Cortex Development-Cellular Architecture Shaped by Biochemical Networks.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Jun 28;11:176. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00176. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28701923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brann A.B, Tcherpakov M, Williams I.M, Futerman A.H, Fainzilber M. Nerve growth factor-induced p75-mediated death of cultured hippocampal neurons is age-dependent and transduced through ceramide generated by neutral sphingomyelinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:9812–9818. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109862200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

