Sensing infection by adenovirus: Toll-like receptor-independent viral DNA recognition signals activation of the interferon regulatory factor 3 master regulator
- PMID: 17251283
- PMCID: PMC1866159
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02685-06
Sensing infection by adenovirus: Toll-like receptor-independent viral DNA recognition signals activation of the interferon regulatory factor 3 master regulator
Abstract
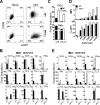
Infection with adenovirus vectors (AdV) results in rapid activation of innate immunity, which serves the dual purpose of stimulating inflammatory antiviral host defenses and the adaptive immune system. Viral recognition by macrophages, dendritic cells, and other cell types requires an ability to sense the presence of a foreign molecular pattern by "pattern recognition receptors." The nature of the adenoviral sensor, the target ligand of the sensor, and the downstream antiviral signaling response triggered by virus infection have not been defined for this nonenveloped double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) virus. We have identified four critical links involved in AdV recognition by murine antigen-presenting cells (APC) and primary lung fibroblasts: (i) viral recognition occurs chiefly via a Toll-like receptor (TLR)-independent nucleic acid-sensing mechanism recognizing the viral dsDNA genome, (ii) the intact viral particle and capsid proteins are required for efficient intracellular delivery of the viral genome, (iii) delivery of the viral genome triggers interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) phosphorylation, and (iv) IRF3 activation is the required dominant antiviral signaling pathway used by APC, whereas the "primary" involvement of NF-kappaB, mitogen-activated protein kinase, or Akt pathways is less prominent. In this study we provide the first direct evidence that infection by a dsDNA virus stimulates an IRF3-mediated interferon and proinflammatory response through a TLR-independent DNA-sensing mechanism.
Figures



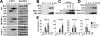

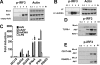
Similar articles
-
Diminished Innate Antiviral Response to Adenovirus Vectors in cGAS/STING-Deficient Mice Minimally Impacts Adaptive Immunity.J Virol. 2016 Jun 10;90(13):5915-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00500-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27076643 Free PMC article.
-
Adenovirus induction of IRF3 occurs through a binary trigger targeting Jun N-terminal kinase and TBK1 kinase cascades and type I interferon autocrine signaling.J Virol. 2009 May;83(9):4081-91. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02591-08. Epub 2009 Feb 11. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19211767 Free PMC article.
-
A Toll-like receptor-independent antiviral response induced by double-stranded B-form DNA.Nat Immunol. 2006 Jan;7(1):40-8. doi: 10.1038/ni1282. Epub 2005 Nov 13. Nat Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16286919
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenovirus sensing by the immune system.Curr Opin Virol. 2016 Dec;21:109-113. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.08.017. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Curr Opin Virol. 2016. PMID: 27639089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diminished Innate Antiviral Response to Adenovirus Vectors in cGAS/STING-Deficient Mice Minimally Impacts Adaptive Immunity.J Virol. 2016 Jun 10;90(13):5915-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00500-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27076643 Free PMC article.
-
Sensing adenovirus infection: activation of interferon regulatory factor 3 in RAW 264.7 cells.J Virol. 2012 Apr;86(8):4527-37. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07071-11. Epub 2012 Feb 15. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22345436 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple innate immune pathways contribute to the immunogenicity of recombinant adenovirus vaccine vectors.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(1):315-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01597-10. Epub 2010 Oct 20. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 20962088 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of signal transduction pathways after transient cutaneous adenoviral gene delivery.BMC Immunol. 2011 Jan 21;12:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-8. BMC Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21255430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergelson, J. M., J. A. Cunningham, G. Droguett, E. A. Kurt-Jones, A. Krithivas, J. S. Hong, M. S. Horwitz, R. L. Crowell, and R. W. Finberg. 1997. Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science 275:1320-1323. - PubMed
-
- Covert, M. W., T. H. Leung, J. E. Gaston, and D. Baltimore. 2005. Achieving stability of lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB activation. Science 309:1854-1857. - PubMed
-
- Genin, P., M. Algarte, P. Roof, R. Lin, and J. Hiscott. 2000. Regulation of RANTES chemokine gene expression requires cooperativity between NF-kappa B and IFN-regulatory factor transcription factors. J. Immunol. 164:5352-5361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

