A novel method for interpretation of T-cell receptor gamma gene rearrangement assay by capillary gel electrophoresis based on normal distribution
- PMID: 17251331
- PMCID: PMC1867425
- DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2007.060032
A novel method for interpretation of T-cell receptor gamma gene rearrangement assay by capillary gel electrophoresis based on normal distribution
Abstract
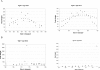
T-cell receptor gamma (TRG) gene rearrangement status is useful for the differential diagnosis of T-cell lesions. The BIOMED-2 protocol that uses two sets of Jgamma and four sets of Vgamma primers in a multiplex, two-tube reaction followed by capillary gel electrophoresis is emerging as a standard assay for this application. Here, we report a computer-aided method to evaluate the significance of a peak in this TRG clonality assay. A best-fit normal distribution (ND) curve and the chi(2) error for each peak are used to determine whether a peak is significantly taller than the background (cutoff for Vgamma(1-8) is 1). Eighty clinical samples that have been previously analyzed by a GC-clamped primer polymerase chain reaction/denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis assay were reanalyzed with the BIOMED-2 assay and scored by the ND method and four previously published methods: relative peak height (RPH), relative peak ratio (RPR), height ratio (HR), and peak height ratio (Rn). A greater than 90% concordance rate was observed between RPH and ND analysis, whereas RPR, Rn, and HR had a lower threshold to call a peak positive. The advantage of the ND method is that it is more objective, reproducible, and can be automated.
Figures
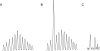

Similar articles
-
Detection of clonal T-cell receptor gamma gene rearrangements using fluorescent-based PCR and automated high-resolution capillary electrophoresis.Mol Diagn. 2001 Sep;6(3):169-79. doi: 10.1054/modi.2001.27056. Mol Diagn. 2001. PMID: 11571710
-
Pseudo-spikes are common in histologically benign lymphoid tissues.J Mol Diagn. 2000 Aug;2(3):145-52. doi: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60630-7. J Mol Diagn. 2000. PMID: 11229519 Free PMC article.
-
A novel clonality assay for the assessment of canine T cell proliferations.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012 Jan 15;145(1-2):410-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2011.12.019. Epub 2011 Dec 28. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2012. PMID: 22237398
-
A rapid restriction fragment length polymorphism polymerase chain reaction-based diagnostic method for identification of T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders.J Surg Res. 1999 Aug;85(2):311-6. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1999.5594. J Surg Res. 1999. PMID: 10423334
-
Comparative investigations of T cell receptor gamma gene rearrangements in frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin wax-embedded tissues by capillary electrophoresis.J Clin Pathol. 2006 Jun;59(6):645-54. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2005.025809. Epub 2006 Feb 6. J Clin Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16461809 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
EuroClonality/BIOMED-2 guidelines for interpretation and reporting of Ig/TCR clonality testing in suspected lymphoproliferations.Leukemia. 2012 Oct;26(10):2159-71. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.246. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Leukemia. 2012. PMID: 22918122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of a worldwide EQA scheme for complex clonality analysis of clinical lymphoproliferative cases demonstrates a learning effect.Virchows Arch. 2021 Aug;479(2):365-376. doi: 10.1007/s00428-021-03046-0. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Virchows Arch. 2021. PMID: 33686511 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of monoclonal immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangement (FR3) in Thai malignant lymphoma by High Resolution Melting curve analysis.Diagn Pathol. 2010 May 19;5:31. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-5-31. Diagn Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20482846 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of a Next-Generation Sequencing-Based T-Cell Receptor Gamma Gene Rearrangement Diagnostic Assay: Transitioning from Capillary Electrophoresis to Next-Generation Sequencing.J Mol Diagn. 2021 Jul;23(7):805-815. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2021.03.008. Epub 2021 Apr 21. J Mol Diagn. 2021. PMID: 33892183 Free PMC article.
-
Assay design affects the interpretation of T-cell receptor gamma gene rearrangements: comparison of the performance of a one-tube assay with the BIOMED-2-based TCRG gene clonality assay.J Mol Diagn. 2010 Nov;12(6):787-96. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2010.090183. J Mol Diagn. 2010. PMID: 20959612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller JE, Wilson SS, Jaye DL, Kronenberg M. An automated semiquantitative B and T cell clonality assay. Mol Diagn. 1999;4:101–117. - PubMed
-
- Simon M, Kind P, Kaudewitz P, Krokowski M, Graf A, Prinz J, Puchta U, Medeiros LJ, Sander CA. Automated high-resolution polymerase chain reaction fragment analysis: a method for detecting T-cell receptor gamma-chain gene rearrangements in lymphoproliferative diseases. Am J Pathol. 1998;152:29–33. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Theodorou I, Bigorgne C, Delfau MH, Lahet C, Cochet G, Vidaud M, Raphael M, Gaulard P, Farcet JP. VJ rearrangements of the TCR gamma locus in peripheral T-cell lymphomas: analysis by polymerase chain reaction and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. J Pathol. 1996;178:303–310. - PubMed
-
- van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Bruggemann M, Evans PA, Hummel M, Lavender FL, Delabesse E, Davi F, Schuuring E, Garcia-Sanz R, van Krieken JH, Droese J, Gonzalez D, Bastard C, White HE, Spaargaren M, Gonzalez M, Parreira A, Smith JL, Morgan GJ, Kneba M, Macintyre EA. Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98–3936. Leukemia. 2003;17:2257–2231. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

