Use of dried spots of whole blood, plasma, and mother's milk collected on filter paper for measurement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 burden
- PMID: 17251400
- PMCID: PMC1829137
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01919-06
Use of dried spots of whole blood, plasma, and mother's milk collected on filter paper for measurement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 burden
Abstract
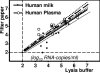
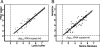
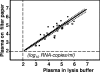
We studied the use of dried spots of bodily fluids (plasma, whole blood, and mother's milk) on filter paper as a means of sample collection and storage for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) viral load testing under stringent field conditions. Plasma placed directly in lysis buffer, which is customarily used for viral load assays, was used for comparison in all our experiments. Utilizing reconstruction experiments, we demonstrate no statistical differences between viral loads determined for plasma and mother's milk spotted on filter paper and those for the same fluids placed directly in lysis buffer. We found that the addition of whole blood directly to lysis buffer was unreliable and could not be considered a feasible option. However, viral load measurements for whole blood spotted onto filter paper correlated with plasma viral load values for both filter spots and lysis buffer (Pearson correlation coefficients, 0.7706 and 0.8155, respectively). In conclusion, dried spots of plasma, whole blood, or mother's milk provide a feasible means for the collection, storage, and shipment of samples for subsequent viral load measurement and monitoring. Virus material spotted and dried on filter paper is a good inexpensive alternative for collecting patient material to monitor the HIV-1 viral load. Measuring the HIV-1 burden from whole blood dried on filter paper provides a suitable alternative for low-technology settings with limited access to refrigeration, as can be found in sub-Saharan Africa.
Figures

References
-
- Akane, A., K. Matsubara, H. Nakamura, S. Takahashi, and K. Kimura. 1994. Identification of the heme compound copurified with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from bloodstains, a major inhibitor of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification. J. Forensic Sci. 39:362-372. - PubMed
-
- Alaeus, A., K. Lidman, A. Sonnerborg, and J. Albert. 1997. Subtype-specific problems with quantification of plasma HIV-1 RNA. AIDS 11:859-865. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Muñoz, M. T., S. Zaragoza-Rodriguez, O. Rojas-Montes, G. Palacios-Saucedo, G. Vazquez-Rosales, A. Gomez-Delgado, J. Torres, and O. Munoz. 2005. High correlation of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 viral load measured in dried-blood spot samples and in plasma under different storage conditions. Arch. Med. Res. 36:382-386. - PubMed
-
- Beckers, C., C. Cornette, B. Francois, and A. Bouckaert. 1979. Screening for neonatal hypothyroidism by thyroxine and thyrotrophin radioimmunoassays using dried blood samples on filter paper. Clin. Endocrinol. 10:567-573. - PubMed
-
- Behets, F., M. Kashamuka, M. Pappaioanou, T. A. Green, R. W. Ryder, V. Batter, J. R. George, W. H. Hannon, and T. C. Quinn. 1992. Stability of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 antibodies in whole blood dried on filter paper and stored under various tropical conditions in Kinshasa, Zaire. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30:1179-1182. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

