Regulation of Akt signaling by D2 and D3 dopamine receptors in vivo
- PMID: 17251429
- PMCID: PMC6672900
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5074-06.2007
Regulation of Akt signaling by D2 and D3 dopamine receptors in vivo
Abstract
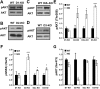
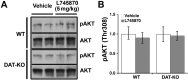
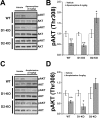
The serine/threonine kinase Akt is a downstream target of dopamine receptor signaling that is inhibited/dephosphorylated in response to direct and indirect dopamine receptor agonists. Although pharmacological studies uncovered the involvement of D2-class dopamine receptors in Akt regulation, they did not identify the role of individual receptor subtypes in this process. Here we used knock-out mice lacking the D1, D2, D2 long, or D3 dopamine receptors as well as a D4 receptor-selective antagonist to address the function of each of these receptors in the regulation of Akt in vivo. Under basal conditions, D2, D2 long, and D3 knock-out mice display enhanced striatal Akt activation, whereas D1 knock-out mice and mice treated with the D4 receptor antagonist L745870 (3-[[4-(4-chlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]methyl]-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine trihydrochloride) have phospho-Akt levels comparable with those of normal control animals. Furthermore, both amphetamine and apomorphine lose their ability to inhibit Akt in D2 knock-out mice but retain their normal effect on this signaling molecule in D1 knock-out animals. Finally, D3 knock-out mice show a reduced sensitivity of Akt-mediated signaling to dopaminergic drugs but retain the action of these drugs on Akt at high dose regimens. These results indicate that D2 receptors are essential for the inhibition of Akt by dopamine and that D3 receptors also participate in this signaling potentially by enhancing D2 receptor response. Identification of the functions of individual dopamine receptor subtypes in Akt regulation may help the development of new pharmaceutical approaches for mental disorders related to abnormal dopamine transmission such as bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.
Figures

References
-
- Angers S, Salahpour A, Bouvier M. Dimerization: an emerging concept for G protein-coupled receptor ontogeny and function. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2002;42:409–435. - PubMed
-
- Baik JH, Picetti R, Saiardi A, Thiriet G, Dierich A, Depaulis A, Le Meur M, Borrelli E. Parkinsonian-like locomotor impairment in mice lacking dopamine D2 receptors. Nature. 1995;377:424–428. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu JM. Not only lithium: regulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by antipsychotics and serotonergic drugs. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007 in press. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu JM, Sotnikova TD, Marion S, Lefkowitz RJ, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG. An Akt/beta-arrestin 2/PP2A signaling complex mediates dopaminergic neurotransmission and behavior. Cell. 2005;122:261–273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
