Cessation of medication for people with schizophrenia already stable on chlorpromazine
- PMID: 17253586
- PMCID: PMC11380555
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006329
Cessation of medication for people with schizophrenia already stable on chlorpromazine
Abstract
Background: Chlorpromazine, one of the first generation of antipsychotic drugs, is effective in the treatment of schizophrenia. For most people schizophrenia is a life-long disorder but about a quarter of those who have a first psychotic breakdown do not go on to experience further breakdowns. Most people with schizophrenia are prescribed antipsychotic drugs, although use is often intermittent. The effects of stopping medication are not well researched in the context of systematic reviews.
Objectives: To quantify the effects of stopping chlorpromazine for people with schizophrenia stable on this drug.
Search strategy: We supplemented an electronic search of the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group Trials Register (March 2006) with reference searching of all identified studies.
Selection criteria: We included all relevant randomised clinical trials.
Data collection and analysis: We independently inspected citations and abstracts, ordered papers and re-inspected and quality assessed these. We independently extracted data and resolved disputes during regular meetings. We analysed dichotomous data using fixed effects relative risk (RR) and the 95% confidence interval (CI). For continuous data, where possible, we calculated the weighted mean difference (WMD). We excluded the data where more than 40% of people were lost to follow up.
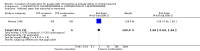
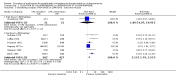
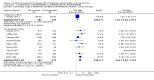
Main results: We included ten trials involving 1042 people with schizophrenia stable on chlorpromazine. Even in the short term, those who remained on chlorpromazine were less likely to experience a relapse compared to people who stopped taking chlorpromazine (n=376, 3 RCTs, RR 6.76 CI 3.37 to 13.54, NNH XX CI XX to XX). Medium term (n=850, 6 RCTs, RR 4.04 CI 2.81 to 5.8, NNH 4 CI 3 to 7) and long term data were similar (n=510, 3 RCTs, RR 1.70 CI 1.44 to 2.01, NNH XX CI XX to XX). People allocated to chlorpromazine withdrawal were not significantly more likely to stay in the study compared with those continuing chlorpromazine treatment (n=374, 1 RCT, RR 1.14 CI 0.55 to 2.35). In sensitivity analyses, there was a significant difference in the 'relapse' outcome between trials for those diagnosed according to checklist criteria compared to those with a clinical diagnosis.
Authors' conclusions: This review confirms clinical experience and quantifies the risks of stopping chlorpromazine medication for a group of people with schizophrenia who are stable on this drug. With its moderate adverse effects, chlorpromazine is likely to remain one of the most widely prescribed treatments for schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



References
References to studies included in this review
Andrews 1976 {published data only}
-
- Andrews P, Hall JN, Snaith RP. A controlled trial of phenothiazine withdrawal in chronic schizophrenic patients. British Journal of Psychiatry 1976;128:451‐55. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Caffey 1964 {published data only}
-
- Caffey EM, Diamond LS, Frank TV, Grasberger JC, Herman L, Klett CJ, Rothstein C. Discontinuation or reduction of chemotherapy in chronic schizophrenics. Journal of Chronic Diseases 1964;17(4):347‐58. [PsycINFO 1965‐09583‐001] - PubMed
-
- Caffey EM, Forrest IS, Frank TV, Klett CJ. Phenothiazine excretion in chronic schizophrenics. American Journal of Psychiatry 1963;120:578‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Freeman 1962 {published data only}
-
- Freeman Leslie S, Alson Eli. Prolonged withdrawal of chlorpromazine in chronic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1962;23:522‐25. [PsycINFO 74‐32161] - PubMed
Greenberg 1966 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg LM, Roth S. Differential effects of abrupt versus gradual withdrawal of chlorpromazine in hospitalized chronic schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1966;123:221‐26. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hogarty 1973 a {published data only}
-
- Goldberg SC, Schooler NR, Hogarty GE, Roper M. Prediction of relapse in schizophrenic outpatients treated by drug and sociotherapy. Archives of General Psychiatry 1977;34(2):171‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hogarty GE, Goldberg SC. Drug and sociotherapy in the aftercare of schizophrenic patients. one‐year relapse rates. Archives of General Psychiatry 1973;28(1):54‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hogarty GE, Goldberg SC, Schooler NR. Drug and sociotherapy in the aftercare of schizophrenic patients. III. Adjustment of non relapsed patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;31(5):609‐18. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hogarty GE, Goldberg SC, Schooler NR, Ulrich RF. Drug and sociotherapy in the aftercare of schizophrenic patients. II two‐year relapse rates. Archives of General Psychiatry 1974;31(5):603‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Hogarty GE, Ulrich RF. Temporal effects of drug and placebo in delaying relapse in schizophrenic outpatients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1977;34(3):297‐301. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mathur 1981 {published data only}
-
- Mathur S, Hall JN. Phenothiazine withdrawal in schizophrenics in a hostel. British Journal of Psychiatry 1981;138:271‐72. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Morton 1968 {published data only}
-
- Morton MR. A study of the withdrawal of chlorpromazine or trifluoperazine in chronic schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1968;124(11):1585‐88. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pigache 1973 {published data only}
-
- Pigache RM. The Clinical relevance of an auditory attention task (PAT) in a longitudinal study of chronic schizophrenia with placebo substitution for chlorpromazine. Schizophrenia research 1993;10(1):39‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Pigache RM, Norris HN. Measurement of drug action in schizophrenia. Clinical Science 1973;44(6):28. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Shawver 1959 {published data only}
-
- Shawver JR, Gorham DR, Leskin LW, Good WW, Kabnick DE. Comparison of chlorpromazine and reserpine in maintenance drug therapy. Diseases of the Nervous System 1959;20:452‐57. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zeller 1956 {published data only}
-
- Zeller WW, Graffagnino PN, Cullen CF, Rietman HJ. Use of chlorpromazine and reserpine in the treatment of emotional disorders. JAMA 1956;160:179‐84. [PsycINFO 81‐02889] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Blackburn 1981 {published data only}
-
- Blackburn HL, Allen JL. Behavioral effects of interrupting and resuming tranquillizing medication among schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1981;133:302‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bouchard 1998 {published data only}
-
- Bouchard RH, Pourcher E, Mérette C, Demers MF, Villeneuve J, Roy MA, Gauthier Y, Cliche D, Labelle A, Maziade M. One year follow up of schizophrenic patients treated with risperidone or classical neuroleptics: a prospective, randomized, multicentered open study. 11th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress; 1998 Oct 31 ‐ Nov 4; Paris, France. 1998. [11th Congress of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology [CD‐ROM]: Conifer, Excerpta Medica Medical Communications BV, 1998 P2124]
Chouinard 1990 {published data only}
-
- Chouinard G. A placebo‐controlled clinical trial of remoxipride and chlorpromazine in newly admitted schizophrenic patients with acute exacerbation. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 1990;358:111‐19. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Crow 1986 {published data only}
-
- Crow TJ, MacMillan JF, Johnson AL, Johnstone EC. A randomised controlled trial of prophylactic neuroleptic treatment. British Journal of Psychiatry 1986;148:120‐27. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Diamond 1960 {published data only}
-
- Diamond LS, Marks JB. Discontinuance of tranquillizers among chronic schizophrenic patients receiving maintenance dosage. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1960;131:247‐51. [PsycINFO 1961‐02332‐001] - PubMed
Garfield 1966 {published data only}
-
- Garfield SL, Gershon S, Sletten I, Neubauer H, Ferrel E. Withdrawal of ataractic medication in schizophrenic patients. Diseases of the Nervous System 1966;27(5):321‐25. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Goldberg 1967 {published data only}
-
- Goldberg SC, Schooler NR, Mattsson N. Paranoid and withdrawal symptoms in schizophrenia: differential symptom reduction over time. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1967;145(2):158‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Good 1958 {published data only}
-
- Good WW, Sterling M, Holtzman WH. Termination of chlorpromazine with schizophrenic patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 1958;115:443‐48. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Mefferd RB Jr, Labrosse EH, Gawienowski AM, Williams RJ. Influence of chlorpromazine on certain biochemical variables of chronic male schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1958;127:167‐79. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gross 1960 {published data only}
-
- Gross M, Hitchman IL, Reeves WP, Lawrence J, Newell PC. Discontinuation of treatment with ataractic drugs. A preliminary report. American Journal of Psychiatry 1960;116:931‐32. - PubMed
Hine 1958 {published data only}
-
- Hine FR. Chlorpromazine in schizophrenic withdrawal and in the withdrawn schizophrenic. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1958;127:220‐27. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hogarty 1973 b {published data only}
-
- Hogarty GE, Munetz MR. Pharmacogenic depression among outpatient schizophrenic patients: a failure to substantiate. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1984;4(1):17‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Howanitz 1996 {published data only}
-
- Howanitz EM, Pardo M, Litwin P, Stern RG, Wainwright KM, FLosonczy M. Efficacy of clozapine versus chlorpromazine in geriatric schizophrenia. 149th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 1996 Oct 2 ‐ May 9; New York, New York, USA. 1996. [MEDLINE: ]
Knight 1979 {published data only}
-
- Knight RG, Harrison A. A double blind comparison of thiothixene and a trifluoperazine‐chlorpromazine composite in the treatment of chronic schizophrenia. New Zealand Medical Journal 1979;89(634):302‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lapolla 1967 {published data only}
-
- Apella A. A double blind evaluation of chlorpromazine versus a combination of perphenazine and amitriptyline. International Journal of Neuropsychiatry 1967;3(5):403‐5. [PsycINFO 1968‐07423‐001]
Levine 1997 {published data only}
-
- Levine J, Caspi N, Laufer N. Immediate effects of chlorpromazine and perphenazine following neuroleptic washout on word association of schizophrenic patients. Schizophrenia Research 1997;26(1):55‐63. [MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO 1997‐06099‐006] - PubMed
Mefferd 1958 {published data only}
-
- Mefferd RBJr, Labrosse EH, Gawienowski AM, Williams RJ. Influence of chlorpromazine on certain biochemical variables of chronic male schizophrenics. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1958;127:167‐79. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Melnyk 1966 {published data only}
-
- Melnyk WT, Worthington AG, Laverty SG. Abrupt withdrawal of chlorpromazine and thioridazine from schizophrenic in‐patients. Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal 1966;11(5):410‐13. [PsycINFO 1966‐13288‐001]
Montero 1971 {published data only}
-
- Montero E. Thioridazine compared with a combination of chlorpromazine and trifluoperazine hydrochloride in schizophrenic patients. 5th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1971 Nov 28 ‐ Dec 4; Mexico City, Mexico. 1971:433. [MEDLINE: ]
Moss 1958 {published data only}
-
- Moss CS, Jensen RE, Morrow W, Freund HG. Specific behavioural changes produced by chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1958;115:449‐51. - PubMed
Pai 2001 {published data only}
-
- Pai YM, Yu SC, Lin CC. Risperidone in reducing tardive dyskinesia: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. 154th Annual Meeting of the American Psychiatric Association; 2001 May 5‐10; New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. Marathon Multimedia, 2001. [MEDLINE: ; PsycINFO 1997‐06099‐006]
Pigache 1993 {published data only}
-
- Pigache RM. Effects of placebo, orphenadrine, and rising doses of chlorpromazine, on PAT performance in chronic schizophrenia. A two year longitudinal study. Schizophrenia Research 1993;10(1):51‐59. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pokorny 1974 {published data only}
-
- Pokorny AD, Prien RF. Lithium in treatment and prevention of effective disorder: a VA NIMH collaborative study. Diseases of the Nervous System 1974;35(7):327‐33. [PsycINFO 53‐03687] - PubMed
Pollack 1956 {published data only}
-
- Pollack B. The effect of chlorpromazine on the return rate of 250 patients released from the Rochester State Hospital. American Journal of Psychiatry 1956;112:937. - PubMed
Prien 1968 {published data only}
-
- Prien RF, Cole JO, Bel kin NF. Relapse in chronic schizophrenics following abrupt withdrawal of tranquillizing medication. British Journal of Psychiatry 1968;115(523):679‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Prien RF, Levine J, Cole JO. Indications for high dose chlorpromazine therapy in chronic schizophrenia. Diseases of the Nervous System 1970;31(11):739‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Schiele 1961 {published data only}
-
- Schiele BC, Vestre ND, Stein KE. A comparison of thioridazine, trifluoperazine, chlorpromazine, and placebo: a double‐blind controlled study on the treatment of chronic hospitalized, schizophrenic patients. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Psychopathology 1961;22(3):151‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Slotnick 1971 {published data only}
-
- Slotnick VB. Management of the acutely agitated psychiatric patient with parental neuroleptics: the comparative symptom effectiveness profiles of haloperidol and chlorpromazine. 5th World Congress of Psychiatry; 1971 Nov 28 ‐ Dec 4; Mexico City, Mexico. 1971:531. [MEDLINE: ]
Troshinsky 1962 {published data only}
-
- Troshinsky C, Aaronson H, Stone RK. Maintenance phenothiazines in aftercare of schizophrenic patients. Pennsylvania Psychiatric Bulletin 1962;2:11‐15.
Wilson 1982 {published data only}
-
- Wilson LG, Roberts RW, Gerber CJ, Johnson MH. Pimozide versus chlorpromazine in chronic schizophrenia ‐ a 52 week double blind study of maintenance therapy. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1982;43(2):62‐5. [PsycINFO 68‐06384] - PubMed
Wode‐Helgodt 1981 {published data only}
-
- Wode‐Helgodt B, Alfredsson G. Concentrations of chlorpromazine and two of its active metabolites in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid of psychotic patients treated with fixed drug doses. Psychopharmacology 1981;73(1):55‐62. [PsycINFO 68‐06384] - PubMed
Additional references
Ahmed 1998
-
- Ahmed I, Soares K, Seifas R, Adams CE. Randomised controlled trials in Archives of General Psychiatry (1959‐1995): a prevalence study. Archives of General Psychiatry 1998;55(8):754‐55. - PubMed
Altman 1996
Bland 1997
Boissel 1999
-
- Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Li W, Chatellier G, Gueyffier F, Buyse M, Boutitie F, Nony P, Haugh M, Mignot G. The problem of therapeutic efficacy indices. 3. Comparison of the indices and their use. Therapie 1999;54(4):405‐11. - PubMed
Caldwell 1992
-
- Caldwell CB, Gottesman II. Schizophrenia ‐ a high‐risk factor for suicide: clues to risk reduction. Suicide and life‐threatening behavior 1992;22:479‐93. - PubMed
Carpenter 1994
-
- Carpenter WT Jr, Buchanan RW. Schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;330:681‐90. - PubMed
CATIE 2005
-
- Lieberman JA, Stroup TS. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 2005;353:1209‐23. - PubMed
Curson 1985
-
- Curson DA, Barnes TR, Bamber RW, Platt SD, Hirsch SR, Duffy JC. Long‐term depot maintenance of chronic schizophrenic out‐patients: the seven year follow‐up of the Medical Research Council fluphenazine/placebo trial. III. Relapse postponement or relapse prevention? The implications for long‐term outcome. British Journal of Psychiatry 1985;146:474‐80. - PubMed
Davis 1975
-
- Davis JM. Overview: maintenance therapy in psychiatry ‐ I. Schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 1975;132:1237‐45. - PubMed
Deeks 2000
-
- Deeks J. Issues in the selection for meta‐analyses of binary data. Abstracts of 8th International Cochrane Colloquium; 2000 Oct 25‐28th; Cape Town, South Africa. 2000.
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazer LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7:623‐29. - PubMed
Donner 2002
-
- Donne A, Klaar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:2971‐80. - PubMed
Essali 1993
-
- Essali MA, Maddocks PD. Seventeen years in the life of a depot neuroleptic clinic ‐ an audit study of schizophrenia and other psychosis. British Journal of Medical Economics 1993;6:3‐11.
Gilbetr 1995
-
- Gilbert PL, Harris J, Adams LA, Jest DV. Neuroleptic withdrawal in schizophrenic patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 1995;52:174‐88. - PubMed
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC, Ukoumunne OC, Chinn S. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy U. ECD EU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. Revised. Rockville: National Institute of Mental Health, 1976.
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2005
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions 4.2.5 [updated May 2005]. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2005, issue 3.
Jusic 1994
-
- Jusic N, Lader M. Post‐mortem antipsychotic drug concentrations and unexplained deaths. British Journal of Psychiatry 1994;165:787‐91. - PubMed
Lorr 1953
-
- Lorr M. The Multidimensional Scale for Rating Psychiatric Patients. Washington D.C.: U.S.V.I, T.B, 1953:19‐507.
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Adams C, Bradley C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales ‐ a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia?. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:249‐52. - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman D. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285(15):1987‐91. - PubMed
NIMH 1964
-
- National Institute of Mental Health. Phenothiazine treatment in schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 1964;10:246‐62. - PubMed
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812.
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias: dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA: Journal of American Medical Association 1995;273:408‐412. - PubMed
Shepherd 1989
-
- Shepherd M, Watt D, Falloon I, et al. The Natural History of Schizophrenia: a five‐year follow‐up study of outcome prediction in a representative sample of schizophrenics.. Psychological Medicine. Monograph supplement 1989;15 (Suppl.):1‐46. - PubMed
Thornley 1998
Thornley 2006
-
- Thornley B, Rathbone J, Adams CE, Awad G. Chlorpromazine versus placebo for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000284.pub2] - DOI
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organisation‐based interventions in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):iii‐92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wing 1961
-
- Wing JK. A simple and reliable sub‐classification of chronic schizophrenia.. The Journal of Mental Science 1961;107:862‐75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

