Asymptotic behaviour and optimal word size for exact and approximate word matches between random sequences
- PMID: 17254306
- PMCID: PMC1764478
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-S5-S21
Asymptotic behaviour and optimal word size for exact and approximate word matches between random sequences
Abstract
Background: The number of k-words shared between two sequences is a simple and efficient alignment-free sequence comparison method. This statistic, D2, has been used for the clustering of EST sequences. Sequence comparison based on D2 is extremely fast, its runtime is proportional to the size of the sequences under scrutiny, whereas alignment-based comparisons have a worst-case run time proportional to the square of the size. Recent studies have tackled the rigorous study of the statistical distribution of D2, and asymptotic regimes have been derived. The distribution of approximate k-word matches has also been studied.
Results: We have computed the D2 optimal word size for various sequence lengths, and for both perfect and approximate word matches. Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests show D2 to have a compound Poisson distribution at the optimal word size for small sequence lengths (below 400 letters) and a normal distribution at the optimal word size for large sequence lengths (above 1600 letters). We find that the D2 statistic outperforms BLAST in the comparison of artificially evolved sequences, and performs similarly to other methods based on exact word matches. These results obtained with randomly generated sequences are also valid for sequences derived from human genomic DNA.
Conclusion: We have characterized the distribution of the D2 statistic at optimal word sizes. We find that the best trade-off between computational efficiency and accuracy is obtained with exact word matches. Given that our numerical tests have not included sequence shuffling, transposition or splicing, the improvements over existing methods reported here underestimate that expected in real sequences. Because of the linear run time and of the known normal asymptotic behavior, D2-based methods are most appropriate for large genomic sequences.
Figures
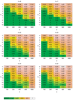
 compared with normal. (adapted from [13]) The letter distribution is fA = fT=
compared with normal. (adapted from [13]) The letter distribution is fA = fT= , fG = fC =
, fG = fC =  , and the diagonal red line in each table is k = 2
, and the diagonal red line in each table is k = 2 n + const.
n + const.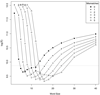
 . The curves show the accuracy of the
. The curves show the accuracy of the  statistics according to the word length and for various mismatches per word. In this simulation, sequence sizes of 600 letters were used. The dotted line shows the results obtained with BLAST.
statistics according to the word length and for various mismatches per word. In this simulation, sequence sizes of 600 letters were used. The dotted line shows the results obtained with BLAST.References
-
- Pearson WR. Rapid and sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:63–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

