Improving the performance of DomainDiscovery of protein domain boundary assignment using inter-domain linker index
- PMID: 17254311
- PMCID: PMC1764483
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-S5-S6
Improving the performance of DomainDiscovery of protein domain boundary assignment using inter-domain linker index
Abstract
Background: Knowledge of protein domain boundaries is critical for the characterisation and understanding of protein function. The ability to identify domains without the knowledge of the structure--by using sequence information only--is an essential step in many types of protein analyses. In this present study, we demonstrate that the performance of DomainDiscovery is improved significantly by including the inter-domain linker index value for domain identification from sequence-based information. Improved DomainDiscovery uses a Support Vector Machine (SVM) approach and a unique training dataset built on the principle of consensus among experts in defining domains in protein structure. The SVM was trained using a PSSM (Position Specific Scoring Matrix), secondary structure, solvent accessibility information and inter-domain linker index to detect possible domain boundaries for a target sequence.
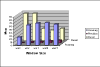
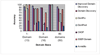
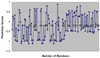
Results: Improved DomainDiscovery is compared with other methods by benchmarking against a structurally non-redundant dataset and also CASP5 targets. Improved DomainDiscovery achieves 70% accuracy for domain boundary identification in multi-domains proteins.
Conclusion: Improved DomainDiscovery compares favourably to the performance of other methods and excels in the identification of domain boundaries for multi-domain proteins as a result of introducing support vector machine with benchmark_2 dataset.
Figures


References
-
- Veretnik S, Shindyalov IN. In: Computational Methods for Domain Partitioning in Protein Structures" in Computational Methods for Protein Structure and Modeling. Xu Y, Xu D, Liang J, editor. Springer-Verlag; 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

