Primary sclerosing cholangitis--the arteriosclerosis of the bile duct?
- PMID: 17254334
- PMCID: PMC1796546
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-6-3
Primary sclerosing cholangitis--the arteriosclerosis of the bile duct?
Abstract
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic inflammatory disease of unknown aetiology affecting the large bile ducts and characterized by periductal fibrosis and stricture formation, which ultimately result in biliary cirrhosis and liver failure. Arteriosclerosis involves the accumulation of altered lipids and lipoproteins in large arteries; this drives inflammation and fibrosis and ultimately leads to narrowing of the arteries and hypoperfusion of dependent organs and tissues. Knowledge of the causative factors is crucial to the understanding of disease mechanisms and the development of specific treatment. Based on pathogenetic similarities between PSC and arteriosclerosis, we hypothesize that PSC represents "arteriosclerosis of the bile duct" initiated by toxic biliary lipids. This hypothesis is based on common molecular, cellular, and morphological features providing the conceptual framework for a deeper understanding of their pathogenesis. This hypothesis should stimulate translational research to facilitate the search for novel treatment strategies for both diseases.
Figures
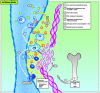
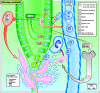
Similar articles
-
Primary sclerosing cholangitis.Semin Gastrointest Dis. 2001 Apr;12(2):103-12. Semin Gastrointest Dis. 2001. PMID: 11352117 Review.
-
Autoimmune diseases of the liver and biliary tract and overlap syndromes in childhood.Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2009 Mar;55(1):53-70. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2009. PMID: 19212308 Review.
-
Animal models for primary sclerosing cholangitis.Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2001 Aug;15(4):591-610. doi: 10.1053/bega.2001.0207. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11492970 Review.
-
Aberrant expression of stem cell factor on biliary epithelial cells and peribiliary infiltration of c-kit-expressing mast cells in hepatolithiasis and primary sclerosing cholangitis: a possible contribution to bile duct fibrosis.J Pathol. 1999 Dec;189(4):609-14. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199912)189:4<609::AID-PATH474>3.0.CO;2-2. J Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10629565
-
24-norUrsodeoxycholic acid is superior to ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of sclerosing cholangitis in Mdr2 (Abcb4) knockout mice.Gastroenterology. 2006 Feb;130(2):465-81. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.10.018. Gastroenterology. 2006. PMID: 16472600
Cited by
-
Hepato-cardiac disorders.World J Hepatol. 2014 Jan 27;6(1):41-54. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i1.41. World J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24653793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medical treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis: a role for novel bile acids and other (post-)transcriptional modulators?Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2009 Feb;36(1):52-61. doi: 10.1007/s12016-008-8085-y. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18751930 Review.
-
Autoimmune liver disease and multiple sclerosis: state of the art and future perspectives.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Nov;23(7):3321-3338. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01128-8. Epub 2023 Jul 8. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37421590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune-mediated cholangiopathies in children: the need to better understand the pathophysiology for finding the future possible treatment targets.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 20;14:1206025. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1206025. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37928553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutting edge issues in primary sclerosing cholangitis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011 Oct;41(2):139-50. doi: 10.1007/s12016-010-8221-3. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21170605
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

