The Toll-like receptor adaptor proteins MyD88 and Mal/TIRAP contribute to the inflammatory and destructive processes in a human model of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17255320
- PMCID: PMC1851858
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060657
The Toll-like receptor adaptor proteins MyD88 and Mal/TIRAP contribute to the inflammatory and destructive processes in a human model of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
The widespread distribution of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and their ligands raises the question whether they contribute to the production of inflammatory and tissue destructive molecules in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We examined the expression and function of TLR2 and TLR4 and their downstream signaling adaptors MyD88 and Mal/TIRAP in synovial membrane cultures from RA tissue. Both TLR2 and TLR4 were detected by flow cytometry, and stimulation with TLR2 and TLR4 ligands augmented the spontaneous production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-8, indicating that TLR2 and TLR4 are functional in these cultures. In addition, overexpression of dominant-negative forms of MyD88 and Mal/TIRAP significantly down-regulated the spontaneous production of cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha, IL-6, and vascular endothelial growth factor, and enzymes MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, and MMP-13 in RA synovial membrane cell cultures. Because TLR2 and TLR4 require both MyD88 and Mal/TIRAP for signaling, this study suggests that TLR function may regulate the expression of these factors in the RA synovium. Conditioned media from synovial membrane cell cultures stimulated human macrophages in a MyD88- and Mal-dependent manner, suggesting the release of a TLR ligand(s) from these cells. Thus, TLRs not only protect against infection but may also promote the inflammatory and destructive process in RA.
Figures
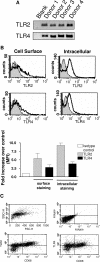

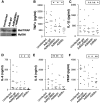
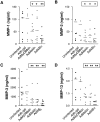
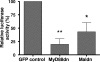
Similar articles
-
Distinct pathways of LPS-induced NF-kappa B activation and cytokine production in human myeloid and nonmyeloid cells defined by selective utilization of MyD88 and Mal/TIRAP.Blood. 2004 Mar 15;103(6):2229-37. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-04-1356. Epub 2003 Nov 20. Blood. 2004. PMID: 14630816
-
MyD88 adapter-like (Mal)/TIRAP interaction with TRAF6 is critical for TLR2- and TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB proinflammatory responses.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24192-203. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.023044. Epub 2009 Jul 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19592497 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role for TIRAP in activation of the signalling cascade shared by TLR2 and TLR4.Nature. 2002 Nov 21;420(6913):324-9. doi: 10.1038/nature01182. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12447441
-
Mal, more than a bridge to MyD88.IUBMB Life. 2013 Sep;65(9):777-86. doi: 10.1002/iub.1201. IUBMB Life. 2013. PMID: 23983209 Review.
-
Mal and MyD88: adapter proteins involved in signal transduction by Toll-like receptors.J Endotoxin Res. 2003;9(1):55-9. doi: 10.1179/096805103125001351. J Endotoxin Res. 2003. PMID: 12691620 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) inhibitors or degraders as therapeutic agents for autoimmune diseases and cancer.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Dec;14(12):5091-5105. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.09.008. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39807338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Innate Immunity for CV Benefit.Drug Discov Today Ther Strateg. 2008;5(1):15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ddstr.2008.05.007. Drug Discov Today Ther Strateg. 2008. PMID: 19430537 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Community series in targeting signalling pathways in inflammatory diseases, volume II.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 27;16:1639004. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1639004. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40655148 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Inhibiting TLR7 Expression in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium Suppresses Experimental Autoimmune Uveitis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 5;12:736261. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.736261. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35069523 Free PMC article.
-
Non-essential role for TLR2 and its signaling adaptor Mal/TIRAP in preserving normal lung architecture in mice.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 29;8(10):e78095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078095. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24205107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Role of cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:397–440. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M, Maini RN. Anti-TNF alpha therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:163–196. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. Pathogen recognition with Toll-like receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17:338–344. - PubMed
-
- Okamura Y, Watari M, Jerud ES, Young DW, Ishizaka ST, Rose J, Chow JC, Strauss JF. The extra domain A of fibronectin activates Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:10229–10233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

