Molecular pathology in the lungs of severe acute respiratory syndrome patients
- PMID: 17255322
- PMCID: PMC1851867
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060469
Molecular pathology in the lungs of severe acute respiratory syndrome patients
Abstract
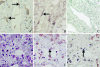
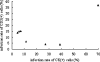
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a novel infectious disease with disastrous clinical consequences, in which the lungs are the major target organs. Previous studies have described the general pathology in the lungs of SARS patients and have identified some of the cell types infected by SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV). However, at the time of this writing, there were no comprehensive reports of the cellular distribution of the virus in lung tissue. In this study, we have performed double labeling combining in situ hybridization with immunohistochemistry and alternating each of these techniques separately in consecutive sections to evaluate the viral distribution on various cell types in the lungs of seven patients affected with SARS. We found that SARS-CoV was present in bronchial epithelium, type I and II pneumocytes, T lymphocytes, and macrophages/monocytes. For pneumocytes, T lymphocytes, and macrophages, the infection rates were calculated. In addition, our present study is the first to demonstrate infection of endothelial cells and fibroblasts in SARS.
Figures


References
-
- Tsang KW, Ho PL, Ooi GC, Yee WK, Wang T, Chan-Yeung M, Lam WK, Seto WH, Yam LY, Cheung TM, Wong PC, Lam B, Ip MS, Chan J, Yuen KY, Lai KN. A cluster of cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1977–1985. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

