Signal transduction pathways of tumor necrosis factor--mediated lung injury induced by ozone in mice
- PMID: 17255564
- PMCID: PMC1899292
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200509-1527OC
Signal transduction pathways of tumor necrosis factor--mediated lung injury induced by ozone in mice
Abstract
Rationale: Increasing evidence suggests that tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha plays a key role in pulmonary injury caused by environmental ozone (O(3)) in animal models and human subjects. We previously determined that mice genetically deficient in TNF response are protected from lung inflammation and epithelial injury after O(3) exposure.
Objectives: The present study was designed to determine the molecular mechanisms of TNF receptor (TNF-R)-mediated lung injury induced by O(3).
Methods: TNF-R knockout (Tnfr(-/-)) and wild-type (Tnfr(+/+)) mice were exposed to 0.3 ppm O(3) or air (for 6, 24, or 48 h), and lung RNA and proteins were prepared. Mice deficient in p50 nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB (Nfkb1(-/-)) or c-Jun-NH(2) terminal kinase 1 (Jnk1(-/-)) and wild-type controls (Nfkb1(+/+), Jnk1(+/+)) were exposed to O(3) (48 h), and the role of NF-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) as downstream effectors of lung injury was analyzed by bronchoalveolar lavage analyses.
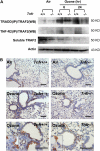
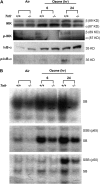
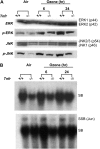
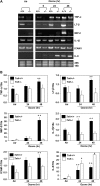
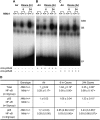
Results: O(3)-induced early activation of TNF-R adaptor complex formation was attenuated in Tnfr(-/-) mice compared with Tnfr(+/+) mice. O(3) significantly activated lung NF-kappaB in Tnfr(+/+) mice before the development of lung injury. Basal and O(3)-induced NF-kappaB activity was suppressed in Tnfr(-/-) mice. Compared with Tnfr(+/+) mice, MAPKs and activator protein (AP)-1 were lower in Tnfr(-/-) mice basally and after O(3). Furthermore, inflammatory cytokines, including macrophage inflammatory protein-2, were differentially expressed in Tnfr(-/-) and Tnfr(+/+) mice after O(3). O(3)-induced lung injury was significantly reduced in Nfkb1(-/-) and Jnk1(-/-) mice relative to respective control animals.
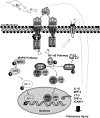
Conclusions: Results suggest that NF-kappaB and MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathways are essential in TNF-R-mediated pulmonary toxicity induced by O(3).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quercetin disrupts tyrosine-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and myeloid differentiation factor-88 association, and inhibits MAPK/AP-1 and IKK/NF-κB-induced inflammatory mediators production in RAW 264.7 cells.Immunobiology. 2013 Dec;218(12):1452-67. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 May 9. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23735482
-
Genetic deletion of PKR abrogates TNF-induced activation of IkappaBalpha kinase, JNK, Akt and cell proliferation but potentiates p44/p42 MAPK and p38 MAPK activation.Oncogene. 2007 Feb 22;26(8):1201-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209906. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16924232
-
Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 contributes to ozone-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in mice.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001 Aug 15;164(4):602-7. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.164.4.2001016. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. PMID: 11520723
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor-Associated Factor Regulation of Nuclear Factor κB and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways.Front Immunol. 2018 Aug 9;9:1849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01849. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30140268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defects in signal transduction pathways in chronic B lymphocytic leukemia cells.Leuk Lymphoma. 1995 Jun;18(1-2):163-70. doi: 10.3109/10428199509064938. Leuk Lymphoma. 1995. PMID: 8580820 Review.
Cited by
-
Promotion of cardiovascular disease by exposure to the air pollutant ozone.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):L205-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00187.2009. Epub 2009 Jun 12. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19525390 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Selenium-Containing Compound Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Regulating the MAPK/AP-1 Pathway.Inflammation. 2021 Dec;44(6):2518-2530. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01521-z. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 34487287
-
Using Multi-objective Optimization to Identify Dynamical Network Biomarkers as Early-warning Signals of Complex Diseases.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 24;6:22023. doi: 10.1038/srep22023. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26906975 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Roles for Notch3 and Notch4 Receptors in Gene Expression and Susceptibility to Ozone-Induced Lung Inflammation in Mice.Environ Health Perspect. 2015 Aug;123(8):799-805. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1408852. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Environ Health Perspect. 2015. PMID: 25658374 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TNFR1 in lung injury and altered lung function induced by the model sulfur mustard vesicant, 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulfide.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011 Feb 1;250(3):245-55. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.10.027. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21070800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peel JL, Tolbert PE, Klein M, Metzger KB, Flanders WD, Todd K, Mulholland JA, Ryan PB, Frumkin H. Ambient air pollution and respiratory emergency department visits. Epidemiology 2005;16:164–174. - PubMed
-
- Tolbert PE, Mulholland JA, MacIntosh DL, Xu F, Daniels D, Devine OJ, Carlin BP, Klein M, Dorley J, Butler AJ, et al. Air quality and pediatric emergency room visits for asthma in Atlanta, Georgia, USA. Am J Epidemiol 2000;151:798–810. - PubMed
-
- Vagaggini B, Taccola M, Cianchetti S, Carnevali S, Bartoli ML, Bacci E, Dente FL, Di Franco A, Giannini D, Paggiaro PL. Ozone exposure increases eosinophilic airway response induced by previous allergen challenge. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;166:1073–1077. - PubMed
-
- Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell 2001;104:487–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

