Trigeminal neuralgia and its management
- PMID: 17255614
- PMCID: PMC1782012
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.39085.614792.BE
Trigeminal neuralgia and its management
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
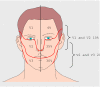

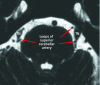

References
-
- Hall GC, Carroll D, Parry D, McQuay HJ. Epidemiology and treatment of neuropathic pain: the UK primary care perspective. Pain 2006;122:156-62. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald BK, Cockerell OC, Sander JW, Shorvon SD. The incidence and lifetime prevalence of neurological disorders in a prospective community-based study in the UK. Brain 2000;123:665-76. - PubMed
-
- Katusic S, Beard CM, Bergstralh E, Kurland LT. Incidence and clinical features of trigeminal neuralgia, Rochester, Minnesota, 1945-1984. Ann Neurol 1990;27:89-95. - PubMed
-
- Headache Classification Subcommitee of the International Headache Society. The international classification of headache disorders. 2nd edition. Cephalalgia 2004;24:1-150. - PubMed
-
- Nurmikko TJ, Eldridge PR. Trigeminal neuralgia—pathophysiology, diagnosis and current treatment. Br J Anaesth 2001;87:117-32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
