Critical role for NF-kappaB-induced JunB in VEGF regulation and tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 17255940
- PMCID: PMC1794395
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601539
Critical role for NF-kappaB-induced JunB in VEGF regulation and tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
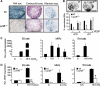
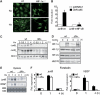
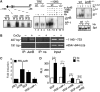
Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression is a complex process involving a plethora of transcriptional regulators. The AP-1 transcription factor is considered as facilitator of hypoxia-induced VEGF expression through interaction with hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) which plays a major role in mediating the cellular hypoxia response. As yet, both the decisive AP-1 subunit leading to VEGF induction and the molecular mechanism by which this subunit is activated have not been deciphered. Here, we demonstrate that the AP-1 subunit junB is a target gene of hypoxia-induced signaling via NF-kappaB. Loss of JunB in various cell types results in severely impaired hypoxia-induced VEGF expression, although HIF is present and becomes stabilized. Thus, we identify JunB as a critical independent regulator of VEGF transcription and provide a mechanistic explanation for the inherent vascular phenotypes seen in JunB-deficient embryos, ex vivo allantois explants and in vitro differentiated embryoid bodies. In support of these findings, tumor angiogenesis was impaired in junB(-/-) teratocarcinomas because of severely impaired paracrine-acting VEGF and the subsequent inability to efficiently recruit host-derived vessels.
Figures
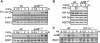
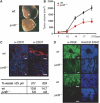

References
-
- Andrecht S, Kolbus A, Hartenstein B, Angel P, Schorpp-Kistner M (2002) Cell cycle promoting activity of JunB through Cyclin A activation. J Biol Chem 277: 35961–35968 - PubMed
-
- Bacon AL, Harris AL (2004) Hypoxia-inducible factors and hypoxic cell death in tumour physiology. Ann Med 36: 530–539 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

