The endothelial glycocalyx: composition, functions, and visualization
- PMID: 17256154
- PMCID: PMC1915585
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-007-0212-8
The endothelial glycocalyx: composition, functions, and visualization
Abstract
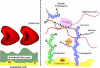
This review aims at presenting state-of-the-art knowledge on the composition and functions of the endothelial glycocalyx. The endothelial glycocalyx is a network of membrane-bound proteoglycans and glycoproteins, covering the endothelium luminally. Both endothelium- and plasma-derived soluble molecules integrate into this mesh. Over the past decade, insight has been gained into the role of the glycocalyx in vascular physiology and pathology, including mechanotransduction, hemostasis, signaling, and blood cell-vessel wall interactions. The contribution of the glycocalyx to diabetes, ischemia/reperfusion, and atherosclerosis is also reviewed. Experimental data from the micro- and macrocirculation alludes at a vasculoprotective role for the glycocalyx. Assessing this possible role of the endothelial glycocalyx requires reliable visualization of this delicate layer, which is a great challenge. An overview is given of the various ways in which the endothelial glycocalyx has been visualized up to now, including first data from two-photon microscopic imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Algenstaedt P, Schaefer C, Biermann T, Hamann A, Schwarzloh B, Greten H, Ruther W, Hansen-Algenstaedt N (2003) Microvascular alterations in diabetic mice correlate with level of hyperglycemia. Diabetes 52:542–549 - PubMed
-
- Ali S, Fritchley SJ, Chaffey BT, Kirby JA (2002) Contribution of the putative heparan sulfate-binding motif BBXB of RANTES to transendothelial migration. Glycobiology 12:535–543 - PubMed
-
- Barker AL, Konopatskaya O, Neal CR, Macpherson JV, Whatmore JL, Winlove CP, Unwin PR, Shore AC (2004) Observation and characterisation of the glycocalyx of viable human endothelial cells using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Phys Chem Chem Phys 6:1006–1011
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

