Telomeric DNA induces apoptosis and senescence of human breast carcinoma cells
- PMID: 17257427
- PMCID: PMC1851376
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr1646
Telomeric DNA induces apoptosis and senescence of human breast carcinoma cells
Abstract
Introduction: Cancer is a leading cause of death in Americans. We have identified an inducible cancer avoidance mechanism in cells that reduces mutation rate, reduces and delays carcinogenesis after carcinogen exposure, and induces apoptosis and/or senescence of already transformed cells by simultaneously activating multiple overlapping and redundant DNA damage response pathways.
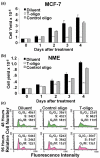
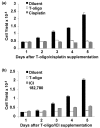
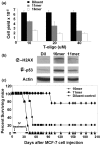
Methods: The human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7, the adriamycin-resistant MCF-7 (Adr/MCF-7) cell line, as well as normal human mammary epithelial (NME) cells were treated with DNA oligonucleotides homologous to the telomere 3' overhang (T-oligos). SCID mice received intravenous injections of MCF-7 cells followed by intravenous administration of T-oligos.
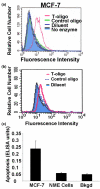
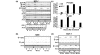
Results: Acting through ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) and its downstream effectors, T-oligos induced apoptosis and senescence of MCF-7 cells but not NME cells, in which these signaling pathways were induced to a far lesser extent. In MCF-7 cells, experimental telomere loop disruption caused identical responses, consistent with the hypothesis that T-oligos act by mimicking telomere overhang exposure. In vivo, T-oligos greatly prolonged survival of SCID mice following intravenous injection of human breast carcinoma cells.
Conclusion: By inducing DNA damage-like responses in MCF-7 cells, T-oligos provide insight into innate cancer avoidance mechanisms and may offer a novel approach to treatment of breast cancer and other malignancies.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Signaling pathway requirements for induction of senescence by telomere homolog oligonucleotides.Exp Cell Res. 2004 Dec 10;301(2):189-200. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.019. Exp Cell Res. 2004. PMID: 15530855
-
Telomere-based DNA damage responses: a new approach to melanoma.FASEB J. 2004 Sep;18(12):1373-81. doi: 10.1096/fj.04-1774com. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15333580
-
Ataxia telangiectasia mutated and p21CIP1 modulate cell survival of drug-induced senescent tumor cells: implications for chemotherapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Mar 15;14(6):1877-87. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4298. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18347191
-
Critical telomere shortening regulated by the ataxia-telangiectasia gene acts as a DNA damage signal leading to activation of p53 protein and limited life-span of human diploid fibroblasts. A review.Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997 Nov;62(11):1306-10. Biochemistry (Mosc). 1997. PMID: 9467855 Review.
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia and cellular responses to DNA damage.Cancer Res. 1995 Dec 15;55(24):5991-6001. Cancer Res. 1995. PMID: 8521380 Review.
Cited by
-
hnRNP C1/C2 and Pur-beta proteins mediate induction of senescence by oligonucleotides homologous to the telomere overhang.Onco Targets Ther. 2013 Dec 18;7:23-32. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S54575. eCollection 2013. Onco Targets Ther. 2013. PMID: 24379680 Free PMC article.
-
T-oligos inhibit growth and induce apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells.Oligonucleotides. 2011 Feb;21(1):47-53. doi: 10.1089/oli.2010.0259. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Oligonucleotides. 2011. PMID: 21281128 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxicity of guanine-based degradation products contributes to the antiproliferative activity of guanine-rich oligonucleotides.Chem Sci. 2015 Jul 1;6(7):3831-3838. doi: 10.1039/c4sc03949a. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Chem Sci. 2015. PMID: 29218153 Free PMC article.
-
Shelterin complex gene: Prognosis and therapeutic vulnerability in cancer.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021 Feb 2;26:100937. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100937. eCollection 2021 Jul. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2021. PMID: 33553693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppressive oligodeoxynucleotides synergistically enhance antiproliferative effects of anticancer drugs in A549 human lung cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2013 Feb;42(2):429-36. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1755. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23291718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, Samuels A, Tiwari RC, Ghafoor A, Feuer EJ, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:10–30. - PubMed
-
- Seidman AD. Systemic treatment of breast cancer. Two decades of progress. Oncology (Williston Park) 2006;20:983–990. discussion 991–982, 997–988. - PubMed
-
- Calvo FA, Meirino RM, Orecchia R. intraoperative radiation therapy part 2. Clinical results. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2006;59:116–127. - PubMed
-
- Hickey BE, Francis D, Lehman MH. Sequencing of chemotherapy and radiation therapy for early breast cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006:CD005212. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

