Expansion of signal transduction by G proteins. The second 15 years or so: from 3 to 16 alpha subunits plus betagamma dimers
- PMID: 17258171
- PMCID: PMC1993906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.12.002
Expansion of signal transduction by G proteins. The second 15 years or so: from 3 to 16 alpha subunits plus betagamma dimers
Abstract
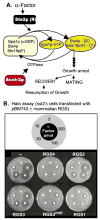
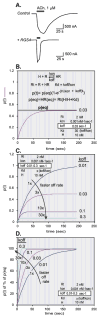
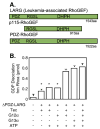
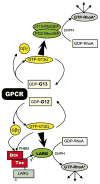
The first 15 years, or so, brought the realization that there existed a G protein coupled signal transduction mechanism by which hormone receptors regulate adenylyl cyclases and the light receptor rhodopsin activates visual phosphodiesterase. Three G proteins, Gs, Gi and transducin (T) had been characterized as alphabetagamma heterotrimers, and Gsalpha-GTP and Talpha-GTP had been identified as the sigaling arms of Gs and T. These discoveries were made using classical biochemical approaches, and culminated in the purification of these G proteins. The second 15 years, or so, are the subject of the present review. This time coincided with the advent of powerful recombinant DNA techniques. Combined with the classical approaches, the field expanded the repertoire of G proteins from 3 to 16, discovered the superfamily of seven transmembrane G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) -- which is not addressed in this article -- and uncovered an amazing repertoire of effector functions regulated not only by alphaGTP complexes but also by betagamma dimers. Emphasis is placed in presenting how the field developed with the hope of conveying why many of the new findings were made.
Figures
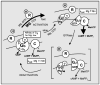
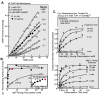
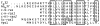
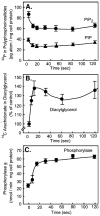

References
-
- Birnbaumer L. The Discovery of Signal Transduction by G Proteins. A personal account and an overview of the initial findings and contributions that led to our present understanding. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembranes. 2007;1768:756–771. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem. 2006.09.027. (in press) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ovchinnikov YA. Rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin: Strucnture-Function Relationships. FEBS Letters. 1982;148:179–191. - PubMed
-
- Dixon RAF, Kobilka BK, Strader DJ, Benovic JL, Dohlman HC, Frielle T, Bolanowski MA, Bennett CD, Rands E, Diehl RE, Mumford RA, Slater EE, Sigal IS, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ, Strader CD. Cloning of the Gene and cDNA for Mammalian Beta-adrenergic Receptor and Homology with Rhodopsin. Nature. 1986;321:75–79. (March 11; published, May issue). - PubMed
-
- Maguire ME, Van Arsdale PM, Gilman AG. An Agonist-Specific Effect of Guanine Nucleotides on Binding to the Beta Adrenergic Receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1976;12:335–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

