BACE1 gene deletion prevents neuron loss and memory deficits in 5XFAD APP/PS1 transgenic mice
- PMID: 17258906
- PMCID: PMC1876698
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2006.12.008
BACE1 gene deletion prevents neuron loss and memory deficits in 5XFAD APP/PS1 transgenic mice
Abstract
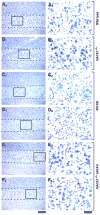
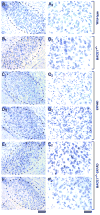
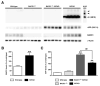
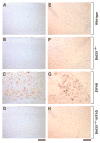
Evidence suggests that beta-amyloid (Abeta) peptide triggers a pathogenic cascade leading to neuronal loss in Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the causal link between Abeta and neuron death in vivo remains unclear since most animal models fail to recapitulate the dramatic cell loss observed in AD. We have recently developed transgenic mice that overexpress human APP and PS1 with five familial AD mutations (5XFAD mice) and exhibit robust neuron death. Here, we demonstrate that genetic deletion of the beta-secretase (BACE1) not only abrogates Abeta generation and blocks amyloid deposition but also prevents neuron loss found in the cerebral cortex and subiculum, brain regions manifesting the most severe amyloidosis in 5XFAD mice. Importantly, BACE1 gene deletion also rescues memory deficits in 5XFAD mice. Our findings provide strong evidence that Abeta ultimately is responsible for neuron death in AD and validate the therapeutic potential of BACE1-inhibiting approaches for the treatment of AD.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A combination Alzheimer's therapy targeting BACE1 and neprilysin in 5XFAD transgenic mice.Mol Brain. 2015 Mar 25;8:19. doi: 10.1186/s13041-015-0110-5. Mol Brain. 2015. PMID: 25884928 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic reductions of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1 and amyloid-beta ameliorate impairment of conditioned taste aversion memory in 5XFAD Alzheimer's disease model mice.Eur J Neurosci. 2010 Jan;31(1):110-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.07031.x. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Eur J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20092558 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of BACE1 haploinsufficiency on APP processing and Aβ concentrations in male and female 5XFAD Alzheimer mice at different disease stages.Neuroscience. 2015 Oct 29;307:128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.08.037. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26314636 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and pharmacological basis for therapeutic inhibition of beta- and gamma-secretases in mouse models of Alzheimer's memory deficits.Rev Neurosci. 2006;17(4):429-54. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2006.17.4.429. Rev Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17139843 Review.
-
beta-Secretase, APP and Abeta in Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2005;38:79-103. Subcell Biochem. 2005. PMID: 15709474 Review.
Cited by
-
CutA divalent cation tolerance homolog (Escherichia coli) (CUTA) regulates β-cleavage of β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) through interacting with β-site APP cleaving protein 1 (BACE1).J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 30;287(14):11141-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.330209. Epub 2012 Feb 17. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22351782 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of receptor tyrosine kinase Tyro3 in amyloidogenic APP processing and β-amyloid deposition in Alzheimer's disease models.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39035. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039035. Epub 2012 Jun 11. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22701746 Free PMC article.
-
Targets and mechanisms of Alpinia oxyphylla Miquel fruits in treating neurodegenerative dementia.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Nov 30;14:1013891. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1013891. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36533181 Free PMC article.
-
miR-128 as a Regulator of Synaptic Properties in 5xFAD Mice Hippocampal Neurons.J Mol Neurosci. 2021 Dec;71(12):2593-2607. doi: 10.1007/s12031-021-01862-2. Epub 2021 Jun 20. J Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34151409
-
Preliminary In Vitro and In Vivo Insights of In Silico Candidate Repurposed Drugs for Alzheimer's Disease.Life (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;13(5):1095. doi: 10.3390/life13051095. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37240740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O’Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T. Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2000;21:383–421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apostolova LG, Dutton RA, Dinov ID, Hayashi KM, Toga AW, Cummings JL, Thompson PM. Conversion of mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer disease predicted by hippocampal atrophy maps. Arch Neurol. 2006;63:693–699. - PubMed
-
- Ashe KH. Learning and memory in transgenic mice modeling Alzheimer’s disease. Learn Mem. 2001;8:301–308. - PubMed
-
- Berger-Sweeney J, McPhie DL, Arters JA, Greenan J, Oster-Granite ML, Neve RL. Impairments in learning and memory accompanied by neurodegeneration in mice transgenic for the carboxyl-terminus of the amyloid precursor protein. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999;66:150–162. - PubMed
-
- Bobinski M, Wegiel J, Tarnawski M, Bobinski M, Reisberg B, de Leon MJ, Miller DC, Wisniewski HM. Relationships between regional neuronal loss and neurofibrillary changes in the hippocampal formation and duration and severity of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1997;56:414–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

