Stomatal development and patterning are regulated by environmentally responsive mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17259259
- PMCID: PMC1820971
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.106.048298
Stomatal development and patterning are regulated by environmentally responsive mitogen-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis
Abstract
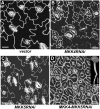
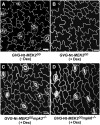
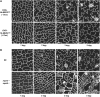
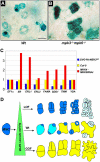
Stomata are specialized epidermal structures that regulate gas (CO(2) and O(2)) and water vapor exchange between plants and their environment. In Arabidopsis thaliana, stomatal development is preceded by asymmetric cell divisions, and stomatal distribution follows the one-cell spacing rule, reflecting the coordination of cell fate specification. Stomatal development and patterning are regulated by both genetic and environmental signals. Here, we report that Arabidopsis MITOGEN-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE3 (MPK3) and MPK6, two environmentally responsive mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), and their upstream MAPK kinases, MKK4 and MKK5, are key regulators of stomatal development and patterning. Loss of function of MKK4/MKK5 or MPK3/MPK6 disrupts the coordinated cell fate specification of stomata versus pavement cells, resulting in the formation of clustered stomata. Conversely, activation of MKK4/MKK5-MPK3/MPK6 causes the suppression of asymmetric cell divisions and stomatal cell fate specification, resulting in a lack of stomatal differentiation. We further establish that the MKK4/MKK5-MPK3/MPK6 module is downstream of YODA, a MAPKKK. The establishment of a complete MAPK signaling cascade as a key regulator of stomatal development and patterning advances our understanding of the regulatory mechanisms of intercellular signaling events that coordinate cell fate specification during stomatal development.
Figures


References
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama, T., and Chua, N.-H. (1997). A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J. 11 605–612. - PubMed
-
- Asai, T., Tena, G., Plotnikova, J., Willmann, M.R., Chiu, W.L., Gomez-Gomez, L., Boller, T., Ausubel, F.M., and Sheen, J. (2002). MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415 977–983. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann, D.C. (2004). Integrating signals in stomatal development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 7 26–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

