OsCSLD1, a cellulose synthase-like D1 gene, is required for root hair morphogenesis in rice
- PMID: 17259288
- PMCID: PMC1820921
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.091546
OsCSLD1, a cellulose synthase-like D1 gene, is required for root hair morphogenesis in rice
Abstract
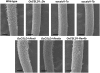
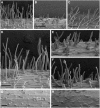
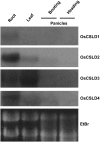
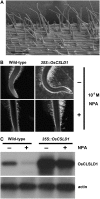
Root hairs are long tubular outgrowths that form on the surface of specialized epidermal cells. They are required for nutrient and water uptake and interact with the soil microflora. Here we show that the Oryza sativa cellulose synthase-like D1 (OsCSLD1) gene is required for root hair development, as rice (Oryza sativa) mutants that lack OsCSLD1 function develop abnormal root hairs. In these mutants, while hair development is initiated normally, the hairs elongate less than the wild-type hairs and they have kinks and swellings along their length. Because the csld1 mutants develop the same density and number of root hairs along their seminal root as the wild-type plants, we propose that OsCSLD1 function is required for hair elongation but not initiation. Both gene trap expression pattern and in situ hybridization analyses indicate that OsCSLD1 is expressed in only root hair cells. Furthermore, OsCSLD1 is the only member of the four rice CSLD genes that shows root-specific expression. Given that the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) gene KOJAK/AtCSLD3 is required for root hair elongation and is expressed in the root hair, it appears that OsCSLD1 may be the functional ortholog of KOJAK/AtCSLD3 and that these two genes represent the root hair-specific members of this family of proteins. Thus, at least part of the mechanism of root hair morphogenesis in Arabidopsis is conserved in rice.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Two poplar cellulose synthase-like D genes, PdCSLD5 and PdCSLD6, are functionally conserved with Arabidopsis CSLD3.J Plant Physiol. 2013 Sep 15;170(14):1267-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2013.04.014. Epub 2013 Jun 5. J Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23746994
-
OsCSLD1 Mediates NH4+-Dependent Root Hair Growth Suppression and AMT1;2 Expression in Rice (Oryza sativa L.).Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 19;11(24):3580. doi: 10.3390/plants11243580. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559692 Free PMC article.
-
OsSNDP1, a Sec14-nodulin domain-containing protein, plays a critical role in root hair elongation in rice.Plant Mol Biol. 2013 May;82(1-2):39-50. doi: 10.1007/s11103-013-0033-4. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Plant Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23456248
-
Root hair development in grasses and cereals (Poaceae).Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017 Aug;45:76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2017.03.009. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017. PMID: 28391059 Review.
-
Building a hair: tip growth in Arabidopsis thaliana root hairs.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2002 Jun 29;357(1422):815-21. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2002.1092. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2002. PMID: 12079677 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Auxin-Glucose Conjugation Protects the Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Seedlings Against Hydroxyurea-Induced Phytotoxicity by Activating UDP-Glucosyltransferase Enzyme.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Feb 16;12:767044. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.767044. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35251058 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association mapping and genomic prediction for late blight and potato cyst nematode resistance in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.).Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 4;14:1211472. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1211472. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37860256 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study reveals the genetic architecture of root hair length in maize.BMC Genomics. 2021 Sep 14;22(1):664. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07961-z. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34521344 Free PMC article.
-
Intragenic complementation at the Lotus japonicus CELLULOSE SYNTHASE-LIKE D1 locus rescues root hair defects.Plant Physiol. 2021 Aug 3;186(4):2037-2050. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab204. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34618101 Free PMC article.
-
The absorption of water from humid air by grass embryos during germination.Plant Physiol. 2022 Jun 27;189(3):1435-1449. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac179. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35512056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chin HG, Choe MS, Lee SH, Park SH, Park SH, Koo JC, Kim NY, Lee JJ, Oh BG, Yi GH, et al (1999) Molecular analysis of rice plants harboring an Ac/Ds transposable element mediated gene trapping system. Plant J 19 615–623 - PubMed
-
- Doblin MS, Kurek I, Jacob-Wilk D, Delmer DP (2002) Cellulose biosynthesis in plants: from genes to rosettes. Plant Cell Physiol 43 1407–1420 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

