Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni biofilms under defined growth conditions
- PMID: 17259368
- PMCID: PMC1828834
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00740-06
Characterization of Campylobacter jejuni biofilms under defined growth conditions
Abstract
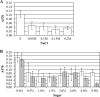
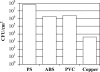
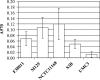
Campylobacter jejuni is a major cause of human diarrheal disease in many industrialized countries and is a source of public health and economic burden. C. jejuni, present as normal flora in the intestinal tract of commercial broiler chickens and other livestock, is probably the main source of human infections. The presence of C. jejuni in biofilms found in animal production watering systems may play a role in the colonization of these animals. We have determined that C. jejuni can form biofilms on a variety of abiotic surfaces commonly used in watering systems, such as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene and polyvinyl chloride plastics. Furthermore, C. jejuni biofilm formation was inhibited by growth in nutrient-rich media or high osmolarity, and thermophilic and microaerophilic conditions enhanced biofilm formation. Thus, nutritional and environmental conditions affect the formation of C. jejuni biofilms. Both flagella and quorum sensing appear to be required for maximal biofilm formation, as C. jejuni flaAB and luxS mutants were significantly reduced in their ability to form biofilms compared to the wild-type strain.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of quorum sensing on flaA transcription and autoagglutination in Campylobacter jejuni.Microbiol Immunol. 2003;47(11):833-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2003.tb03449.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14638994
-
Role of flgA for Flagellar Biosynthesis and Biofilm Formation of Campylobacter jejuni NCTC11168.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Nov;25(11):1871-9. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1504.04080. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26215271
-
Adhesion, Biofilm Formation, and luxS Sequencing of Campylobacter jejuni Isolated From Water in the Czech Republic.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Nov 16;10:596613. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.596613. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33330139 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Campylobacter Biofilm Formation and Quorum Sensing.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2021;431:293-319. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-65481-8_11. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33620656 Review.
-
Does Campylobacter jejuni form biofilms in food-related environments?Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Sep;80(17):5154-60. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01493-14. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24928882 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Trans-cinnamaldehyde nanoemulsion reduces Salmonella Enteritidis biofilm on steel and plastic surfaces and downregulates expression of biofilm associated genes.Poult Sci. 2025 May;104(5):105086. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105086. Epub 2025 Mar 22. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40168703 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA chaperone Hfq is important for growth and stress tolerance in Francisella novicida.PLoS One. 2011 May 5;6(5):e19797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019797. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21573133 Free PMC article.
-
Transducer like proteins of Campylobacter jejuni 81-176: role in chemotaxis and colonization of the chicken gastrointestinal tract.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 May 27;5:46. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00046. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26075188 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of sequential Campylobacter jejuni 81-176 lipooligosaccharide core truncations on biofilm formation, stress survival, and pathogenesis.J Bacteriol. 2010 Apr;192(8):2182-92. doi: 10.1128/JB.01222-09. Epub 2010 Feb 5. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20139192 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm Formation and Motility Are Promoted by Cj0588-Directed Methylation of rRNA in Campylobacter jejuni.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jan 18;7:533. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00533. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29404277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aydin, F., H. I. Atabay, and M. Akan. 2001. The isolation and characterization of Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni from domestic geese (Anser anser). J. Appl. Microbiol. 90:637-642. - PubMed
-
- Baker, J., M. D. Barton, and J. Lanser. 1999. Campylobacter species in cats and dogs in South Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 77:662-666. - PubMed
-
- Blaser, M. J., I. D. Berkowitz, F. M. LaForce, J. Cravens, L. B. Reller, and W. L. Wang. 1979. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann. Intern. Med. 91:179-185. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

