Examination of Ligand-Dependent Coactivator Recruitment by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-alpha (PPARalpha)
- PMID: 17259669
- PMCID: PMC1664713
- DOI: 10.1155/PPAR/2006/69612
Examination of Ligand-Dependent Coactivator Recruitment by Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-alpha (PPARalpha)
Abstract
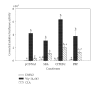
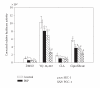
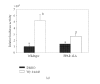
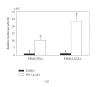
The ligand-dependent recruitment of coactivators to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPARalpha) was examined. PPAR-binding protein (PBP), PPARgamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha), steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1), and CBP/p300-interacting transactivator with ED-rich tail 2 (CITED2) affected PPARalpha activity in the presence of Wy-14,643. The effects on PPARalpha activity in light of increased or decreased expression of these coactivators were qualitatively different depending on the ligand examined. Diminished expression of PGC-1alpha, SRC-1, or PBP by RNAi plasmids affected natural or synthetic agonist activity whereas only Wy-14,643 was affected by decreased PGC-1alpha. The interaction of PPARalpha with an LXXLL-containing peptide library showed ligand-specific patterns, indicative of differences in conformational change. The association of coactivators to PPARalpha occurs predominantly via the carboxyl-terminus and mutating (456)LHPLL to (456)LHPAA resulted in a dominant-negative construct. This research confirms that coactivator recruitment to PPARalpha is ligand-dependent and that selective receptor modulators (SRMs) of this important protein are likely.
Figures

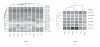




Similar articles
-
Identification of the CREB-binding protein/p300-interacting protein CITED2 as a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha coregulator.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jun 4;279(23):24053-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401489200. Epub 2004 Mar 29. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15051727
-
Ligand and coactivator recruitment preferences of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002 Jul;81(3):217-25. doi: 10.1016/s0960-0760(02)00066-3. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 12163133
-
Different Coactivator Recruitment to Human PPARα/δ/γ Ligand-Binding Domains by Eight PPAR Agonists to Treat Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 11;12(3):624. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030624. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540237 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products, PGC-1 α , and Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020 May;10(5):734-745. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.01.001. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020. PMID: 32528825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, coactivators, and downstream targets.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2000;32 Spring:187-204. doi: 10.1385/cbb:32:1-3:187. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 11330046 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of PPARalpha modifies fatty acid effects on insulin secretion in uncoupling protein-2 knockout mice.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2007 Mar 6;4:6. doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-4-6. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2007. PMID: 17341307 Free PMC article.
-
PPAR-gamma agonists inhibit TGF-beta1-induced chemokine expression in human tubular epithelial cells.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009 Jan;30(1):107-12. doi: 10.1038/aps.2008.15. Epub 2008 Dec 22. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009. PMID: 19098936 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of PPAR activity via phosphorylation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Aug;1771(8):952-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.04.018. Epub 2007 May 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17560826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole genome association study identifies regions of the bovine genome and biological pathways involved in carcass trait performance in Holstein-Friesian cattle.BMC Genomics. 2014 Oct 1;15(1):837. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-837. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25273628 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse Cardiac Pde1C Is a Direct Transcriptional Target of Pparα.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 22;19(12):3704. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123704. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30469494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dreyer C, Krey G, Keller H, Givel F, Helftenbein G, Wahli W. Control of the peroxisomal β-oxidation pathway by a novel family of nuclear hormone receptors. Cell. 1992;68(5):879–887. - PubMed
-
- Roberts RA, James NH, Woodyatt NJ, Macdonald N, Tugwood JD. Evidence for the suppression of apoptosis by the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARα) Carcinogenesis. 1998;19(1):43–48. - PubMed
-
- James NH, Gill JH, Brindle R, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) alpha-regulated growth responses and their importance to hepatocarcinogenesis. Toxicology Letters. 1998;102-103:91–96. - PubMed
-
- Olson MJ. DNA strand breaks induced by hydrogen peroxide in isolated rat hepatocytes. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. 1988;23(3):407–423. - PubMed
-
- Reddy JK, Rao MS. Oxidative DNA damage caused by persistent peroxisome proliferation: its role in hepatocarcinogenesis. Mutation Research. 1989;214(1):63–68. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

