Intravenous immune globulin in hereditary inclusion body myopathy: a pilot study
- PMID: 17261181
- PMCID: PMC1790898
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2377-7-3
Intravenous immune globulin in hereditary inclusion body myopathy: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Hereditary Inclusion Body Myopathy (HIBM) is an autosomal recessive, adult onset, non-inflammatory neuromuscular disorder with no effective treatment. The causative gene, GNE, codes for UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase, which catalyzes the first two reactions in the synthesis of sialic acid. Reduced sialylation of muscle glycoproteins, such as alpha-dystroglycan and neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM), has been reported in HIBM.
Methods: We treated 4 HIBM patients with intravenous immune globulin (IVIG), in order to provide sialic acid, because IgG contains 8 micromol of sialic acid/g. IVIG was infused as a loading dose of 1 g/kg on two consecutive days followed by 3 doses of 400 mg/kg at weekly intervals.
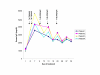
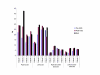
Results: For all four patients, mean quadriceps strength improved from 19.0 kg at baseline to 23.2 kg (+22%) directly after IVIG loading to 25.6 kg (+35%) at the end of the study. Mean shoulder strength improved from 4.1 kg at baseline to 5.9 kg (+44%) directly after IVIG loading to 6.0 kg (+46%) at the end of the study. The composite improvement for 8 other muscle groups was 5% after the initial loading and 19% by the end of the study. Esophageal motility and lingual strength improved in the patients with abnormal barium swallows. Objective measures of functional improvement gave variable results, but the patients experienced improvements in daily activities that they considered clinically significant. Immunohistochemical staining and immunoblotting of muscle biopsies for alpha-dystroglycan and NCAM did not provide consistent evidence for increased sialylation after IVIG treatment. Side effects were limited to transient headaches and vomiting.
Conclusion: The mild benefits in muscle strength experienced by HIBM patients after IVIG treatment may be related to the provision of sialic acid supplied by IVIG. Other sources of sialic acid are being explored as treatment options for HIBM.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The hereditary inclusion body myopathy enigma and its future therapy.Neurotherapeutics. 2008 Oct;5(4):633-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2008.07.004. Neurotherapeutics. 2008. PMID: 19019317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum neural cell adhesion molecule is hyposialylated in hereditary inclusion body myopathy.Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2012 May;16(5):313-7. doi: 10.1089/gtmb.2011.0146. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2012. PMID: 22085395
-
Hypoglycosylation of alpha-dystroglycan in patients with hereditary IBM due to GNE mutations.Mol Genet Metab. 2004 Mar;81(3):196-202. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2003.11.012. Mol Genet Metab. 2004. PMID: 14972325
-
Hereditary inclusion body myopathy: single patient response to intravenous dosing of GNE gene lipoplex.Hum Gene Ther. 2011 Nov;22(11):1331-41. doi: 10.1089/hum.2010.192. Epub 2011 Apr 25. Hum Gene Ther. 2011. PMID: 21517694 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary inclusion-body myopathy with sparing of the quadriceps: the many tiles of an incomplete puzzle.Acta Myol. 2011 Oct;30(2):91-5. Acta Myol. 2011. PMID: 22106710 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GNE myopathy: History, etiology, and treatment trials.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 18;13:1002310. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.1002310. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36330422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical assessment of wt GNE gene plasmid for management of hereditary inclusion body myopathy 2 (HIBM2).Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2008 Jun 20;2:243-52. doi: 10.4137/grsb.s728. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2008. PMID: 19787087 Free PMC article.
-
GNE Myopathy: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Challenges.Neurotherapeutics. 2018 Oct;15(4):900-914. doi: 10.1007/s13311-018-0671-y. Neurotherapeutics. 2018. PMID: 30338442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The hereditary inclusion body myopathy enigma and its future therapy.Neurotherapeutics. 2008 Oct;5(4):633-7. doi: 10.1016/j.nurt.2008.07.004. Neurotherapeutics. 2008. PMID: 19019317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological, Physiochemical, and Drug-Relevant Biological Properties of Short Chain Fatty Acid Hexosamine Analogues Used in Metabolic Glycoengineering.Mol Pharm. 2018 Mar 5;15(3):705-720. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00525. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Mol Pharm. 2018. PMID: 28853901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sivakuma K, Dalakas MC. The spectrum of familial inclusion body myopathies in 13 families and description of a quadriceps sparing phenotype in non Iranian Jews. Neurology. 1996;47:977–984. - PubMed
-
- Argov Z, Eisenberg I, Grabov-Nardini G, Sadeh M, Wirguin I, Soffer D, Mitrani-Rosenbaum S. Hereditary inclusion body myopathy. The Middle Eastern genetic cluster. Neurology. 2003;60:1519–1523. - PubMed
-
- Eisenberg I, Avidan N, Potikha T, Hochner H, Chen M, Olender T, Barash M, Shemesh M, Sadeh M, Grabov-Nardini G, Shmilevich I, Friedmann A, Karpati , Bradley WG, Baumbach L, Lancet D, Asher EB, Beckmann JS, Argov Z, Mitrani-Rosenbaum S. The UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase gene is mutated in hereditary inclusion body myopathy. Nat Genet. 2001;29:83–89. doi: 10.1038/ng718. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

