Development of genomic array footprinting for identification of conditionally essential genes in Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 17261526
- PMCID: PMC1828782
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01900-06
Development of genomic array footprinting for identification of conditionally essential genes in Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a major cause of serious infections such as pneumonia and meningitis in both children and adults worldwide. Here, we describe the development of a high-throughput, genome-wide technique, genomic array footprinting (GAF), for the identification of genes essential for this bacterium at various stages during infection. GAF enables negative screens by means of a combination of transposon mutagenesis and microarray technology for the detection of transposon insertion sites. We tested several methods for the identification of transposon insertion sites and found that amplification of DNA adjacent to the insertion site by PCR resulted in nonreproducible results, even when combined with an adapter. However, restriction of genomic DNA followed directly by in vitro transcription circumvented these problems. Analysis of parallel reactions generated with this method on a large mariner transposon library showed that it was highly reproducible and correctly identified essential genes. Comparison of a mariner library to one generated with the in vivo transposition plasmid pGh:ISS1 showed that both have an equal degree of saturation but that 9% of the genome is preferentially mutated by either one. The usefulness of GAF was demonstrated in a screen for genes essential for surviving zinc stress. This identified a gene encoding a putative cation efflux transporter, and its deletion resulted in an inability to grow under high-zinc conditions. In conclusion, we developed a fast, versatile, specific, and high-throughput method for the identification of conditionally essential genes in S. pneumoniae.
Figures


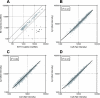
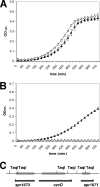
Similar articles
-
Search for genes essential for pneumococcal transformation: the RADA DNA repair protein plays a role in genomic recombination of donor DNA.J Bacteriol. 2007 Sep;189(18):6540-50. doi: 10.1128/JB.00573-07. Epub 2007 Jul 13. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17631629 Free PMC article.
-
Selection analyses of insertional mutants using subgenic-resolution arrays.Nat Biotechnol. 2001 Nov;19(11):1060-5. doi: 10.1038/nbt1101-1060. Nat Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11689852
-
Genome-wide identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae genes essential for bacterial replication during experimental meningitis.Infect Immun. 2011 Jan;79(1):288-97. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00631-10. Epub 2010 Nov 1. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21041497 Free PMC article.
-
Using genomic microarrays to study insertional/transposon mutant libraries.Methods Enzymol. 2007;421:90-110. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)21010-3. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17352918 Review.
-
Screening transposon mutant libraries using full-genome oligonucleotide microarrays.Methods Enzymol. 2007;421:110-25. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)21011-5. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17352919 Review.
Cited by
-
CodY of Streptococcus pneumoniae: link between nutritional gene regulation and colonization.J Bacteriol. 2008 Jan;190(2):590-601. doi: 10.1128/JB.00917-07. Epub 2007 Nov 16. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18024519 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive identification of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium genes required for infection of BALB/c mice.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Jul;5(7):e1000529. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000529. Epub 2009 Jul 31. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19649318 Free PMC article.
-
Two DHH subfamily 1 proteins contribute to pneumococcal virulence and confer protection against pneumococcal disease.Infect Immun. 2011 Sep;79(9):3697-710. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01383-10. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21768284 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing CRISPR-Cas9 for Genome Editing in Streptococcus pneumoniae D39V.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Feb 26;87(6):e02762-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02762-20. Print 2021 Feb 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33397704 Free PMC article.
-
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae carbonic anhydrase is important for environmental and intracellular survival.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jun;195(12):2737-46. doi: 10.1128/JB.01870-12. Epub 2013 Apr 5. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23564172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Autret, N., and A. Charbit. 2005. Lessons from signature-tagged mutagenesis on the infectious mechanisms of pathogenic bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29:703-717. - PubMed
-
- Bogaert, D., R. de Groot, and P. W. Hermans. 2004. Streptococcus pneumoniae colonisation: the key to pneumococcal disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 4:144-154. - PubMed
-
- Carver, T. E., B. Bordeau, M. D. Cummings, E. C. Petrella, M. J. Pucci, L. E. Zawadzke, B. A. Dougherty, J. A. Tredup, J. W. Bryson, J. Yanchunas, Jr., M. L. Doyle, M. R. Witmer, M. I. Nelen, R. L. DesJarlais, E. P. Jaeger, H. Devine, E. D. Asel, B. A. Springer, R. Bone, F. R. Salemme, and M. J. Todd. 2005. Decrypting the biochemical function of an essential gene from Streptococcus pneumoniae using ThermoFluor technology. J. Biol. Chem. 280:11704-11712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

