Activated complement components and complement activator molecules on the surface of cell-derived microparticles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and healthy individuals
- PMID: 17261534
- PMCID: PMC1954699
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.061309
Activated complement components and complement activator molecules on the surface of cell-derived microparticles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and healthy individuals
Abstract
Objectives: In vitro, microparticles can activate complement via the classical pathway. If demonstrable ex vivo, this mechanism may contribute to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We therefore investigated the presence of activated complement components and complement activator molecules on the surface of cell-derived microparticles of RA patients and healthy individuals.
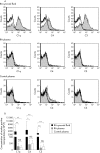
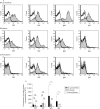
Methods: Microparticles from synovial fluid (n = 8) and plasma (n = 9) of 10 RA patients and plasma of sex- and age-matched healthy individuals (n = 10) were analysed by flow cytometry for bound complement components (C1q, C4, C3) and complement activator molecules (C-reactive protein (CRP), serum amyloid P component (SAP), immunoglobulin (Ig) M, IgG).
Results: Microparticles with bound C1q, C4, and/or C3 were abundant in RA synovial fluid, while in RA and control plasma much lower levels were present. Microparticles with bound C1q correlated with those with bound C3 in synovial fluid (r = 0.961, p = 0.0001), and with those with bound C4 in plasma (RA: r = 0.908, p = 0.0007; control: r = 0.632, p = 0.0498), indicating classical pathway activation. In synovial fluid, microparticles with IgM and IgG correlated with those with C1q (r = 0.728, p = 0.0408; r = 0.952, p = 0.0003, respectively), and in plasma, microparticles with CRP correlated with those with C1q (RA: r = 0.903, p = 0.0021; control: r = 0.683, p = 0.0296), implicating IgG and IgM in the classical pathway activation in RA synovial fluid, and CRP in the low level classical pathway activation in plasma.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates the presence of bound complement components and activator molecules on microparticles ex vivo, and supports their role in low grade complement activation in plasma and increased complement activation in RA synovial fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
References
-
- Distler J H, Pisetsky D S, Huber L C, Kalden J R, Gay S, Distler O. Microparticles as regulators of inflammation: novel players of cellular crosstalk in the rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum 2005523337–3348. - PubMed
-
- Mollnes T E, Lea T, Mellbye O J, Pahle J, Grand O, Harboe M. Complement activation in rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by C3dg and the terminal complement complex. Arthritis Rheum 198629715–721. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous