In vitro and in vivo activities of PD 0305970 and PD 0326448, new bacterial gyrase/topoisomerase inhibitors with potent antibacterial activities versus multidrug-resistant gram-positive and fastidious organism groups
- PMID: 17261623
- PMCID: PMC1855495
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01321-06
In vitro and in vivo activities of PD 0305970 and PD 0326448, new bacterial gyrase/topoisomerase inhibitors with potent antibacterial activities versus multidrug-resistant gram-positive and fastidious organism groups
Abstract
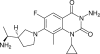
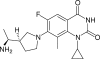
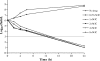
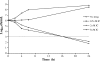
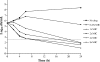
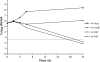
PD 0305970 and PD 0326448 are new bacterial gyrase and topoisomerase inhibitors (quinazoline-2,4-diones) that possess outstanding in vitro and in vivo activities against a wide spectrum of bacterial species including quinolone- and multidrug-resistant gram-positive and fastidious organism groups. The respective MICs (microg/ml) for PD 0305970 capable of inhibiting>or=90% of bacterial strains tested ranged from 0.125 to 0.5 versus staphylococci, 0.03 to 0.06 versus streptococci, 0.25 to 2 versus enterococci, and 0.25 to 0.5 versus Moraxella catarrhalis, Haemophilus influenzae, Listeria monocytogenes, Legionella pneumophila, and Neisseria spp. PD 0326448 MIC90s were generally twofold higher versus these same organism groups. Comparative quinolone MIC90 values were 4- to 512-fold higher than those of PD 0305970. In testing for frequency of resistance, PD 0305970 and levofloxacin showed low levels of development of spontaneous resistant mutants versus both Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Unlike quinolones, which target primarily gyrA and parC, analysis of resistant mutants in S. pneumoniae indicates that the likely targets of PD 0305970 are gyrB and parE. PD 0305970 demonstrated rapid bactericidal activity by in vitro time-kill testing versus streptococci. This bactericidal activity carried over to in vivo testing, where PD 0305970 and PD 0326448 displayed outstanding Streptococcus pyogenes 50% protective doses (PD50s) (oral dosing) of 0.7 and 3.6 mg/kg, respectively (ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin PD50s were>100 and 17.7 mg/kg, respectively). PD 0305970 was also potent in a pneumococcal pneumonia mouse infection model (PD50=3.2 mg/kg) and was 22-fold more potent than levofloxacin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities of heteroaryl isothiazolones against resistant gram-positive pathogens.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Apr;51(4):1259-67. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01315-06. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17242152 Free PMC article.
-
Novel DNA gyrase inhibitors: microbiological characterisation of pyrrolamides.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013 Jan;41(1):28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.08.017. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013. PMID: 23142086
-
Novel topoisomerase inhibitors: microbiological characterisation and in vivo efficacy of pyrimidines.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013 Apr;41(4):363-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.12.001. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2013. PMID: 23305654
-
DNA gyrase inhibitors: Progress and synthesis of potent compounds as antibacterial agents.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jul;103:923-938. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.021. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29710509 Review.
-
Fluoroquinolone resistance among Gram-positive cocci.Lancet Infect Dis. 2002 Sep;2(9):530-8. doi: 10.1016/s1473-3099(02)00369-9. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002. PMID: 12206969 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of Qnr on agents other than quinolones that target DNA gyrase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Nov;59(11):6689-95. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01292-15. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 26239981 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Synthesis of the 2-amino-6-chloro-4-cyclopropyl-7-fluoro-5-methoxy-pyrido[1,2-c]pyrimidine-1,3-dione core ring system.Tetrahedron Lett. 2009 Feb 18;50(7):785-789. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.11.121. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009. PMID: 20160840 Free PMC article.
-
Development and characterisation of highly antibiotic resistant Bartonella bacilliformis mutants.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 26;6:33584. doi: 10.1038/srep33584. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27667026 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure and stability of gyrase-fluoroquinolone cleaved complexes from Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 16;113(7):1706-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1525047113. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26792525 Free PMC article.
-
Quinazoline-2,4(1H, 3H)-diones inhibit the growth of multiple human tumor cell lines.Mol Divers. 2013 May;17(2):197-219. doi: 10.1007/s11030-012-9421-y. Epub 2013 Jan 26. Mol Divers. 2013. PMID: 23354539
References
-
- Bassetti, M., G. Melica, A. Di Biagio, E. Righi, R. Rosso, and D. Bassetti. 2004. New antibiotics for treatment of serious infections due to antibiotic-resistant gram-positive cocci. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 15:109-117.
-
- Cohen, M. A., M. D. Huband, S. L. Yoder, J. W. Gage, and G. E. Roland. 1998. Bacterial eradication by clinafloxacin, CI-990, and ciprofloxacin employing MBC test, in-vitro time-kill and in vivo time-kill studies. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 41:605-614. - PubMed
-
- Coleman, K. 2004. Recent advances in the treatment of gram-positive infections. Drug Discov. Today 1:455-460.
-
- Edelstein, P. H., M. A. C. Edelstein, J. Weidenfeld, and M. B. Dorr. 1990. In vitro activity of sparfloxacin (CI-978; AT-4140) for clinical Legionella isolates, pharmacokinetics in guinea pigs, and use to treat guinea pigs with L. pneumophila pneumonia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 34:2122-2127. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous