A systematic review on clinical management of antipsychotic-induced sexual dysfunction in schizophrenia
- PMID: 17262163
- PMCID: PMC11068300
- DOI: 10.1590/s1516-31802006000500012
A systematic review on clinical management of antipsychotic-induced sexual dysfunction in schizophrenia
Abstract
Introduction: Sexual dysfunction frequently occurs in patients with schizophrenia under antipsychotic therapy, and the presence of sexual side effects may affect compliance. The aim of this study was to review and describe clinical findings relating to the appropriate management of such dysfunctions.
Material and methods: The research was carried out through Medline (from 1966 to March 2005), PsycInfo (from 1974 to March 2005), and Cochrane Library (from 1965 to March 2005) and included any kind of study, from case reports to randomized trials.
Results: The most common sexual dysfunctions found in the literature were libido decrease, difficulties in achieving and maintaining erection, ejaculatory dysfunction, orgasmic dysfunction, and menstrual irregularities. Thirteen papers were found: eight of them were open-label studies, four were descriptions of cases, and only one was a randomized clinical trial. All of them were short-term and had small sample sizes. The agents used were: bromocriptine, cabergoline, cyproheptadine, amantadine, shakuyaku-kanzo-to, sildenafil and selegiline.
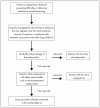
Discussion: There was no evidence that those agents had proper efficacy in treating the antipsychotic-induced sexual dysfunction. An algorithm for managing sexual dysfunction induced by antipsychotics is suggested as a support for clinical decisions. Since the outcome from schizophrenia treatment is strongly related to compliance with the antipsychotics, prevention of sexual dysfunction is better than its treatment, since there is a scarcity of data available regarding the efficacy of intervention to deal with these problems.
INTRODUÇÃO:: Disfunção sexual freqüentemente ocorre em pacientes com esquizofrenia em terapia com antipsicóticos e a presença de efeitos adversos sexuais pode afetar a adesão ao tratamento. O objetivo do estudo é rever e descrever achados clínicos relacionados ao manejo apropriado de tais disfunções.
MATERIAIS E MÉTODOS:: A pesquisa foi feita pelo Medline (de 1966 a março de 2005), PsycInfo (de 1974 a março de 2005) e Biblioteca Cochrane (de 1965 a março de 2005) e incluiu qualquer tipo de desenho de estudo de relato de caso a estudos clínicos randomizados.
RESULTADOS:: As disfunções sexuais mais comuns encontradas na literatura foram diminuição da libido, dificuldades em alcançar e manter ereção, disfunção ejaculatória, orgásmica e irregularidades menstruais. Treze artigos foram encontrados: oito deles eram estudos abertos, quatro descrições de casos e somente um estudo clínico randomizado. Todos eram de curta duração e com tamanho de amostra pequeno. Os agentes usados foram: bromocriptina, cabergolina, ciproheptadina, amantadina, shakuyaku-kanzo-to, sildenafil e selegilina.
DISCUSSÃO:: Não há evidências de eficácia apropriada destes agentes no tratamento da disfunção sexual induzida por antipsicóticos. Um algoritmo foi sugerido para manejo da disfunção sexual induzida por antipsicóticos, suportando decisões clínicas. Como o desfecho da esquizofrenia é fortemente relacionado a adesão ao tratamento com antipsicóticos, a prevenção da disfunção sexual é melhor que seu tratamento, visto que muito poucos dados estão disponíveis sobre a eficácia de intervenções destes problemas.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Benzodiazepines for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jan 24;(1):CD006391. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006391. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11:CD006391. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006391.pub2. PMID: 17253592 Updated.
-
Lithium for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(3):CD003834. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003834. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD003834. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003834.pub2. PMID: 12917990 Updated.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Antipsychotics for schizophrenia spectrum disorders with catatonic symptoms.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7(7):CD013100. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013100.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35844143 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Management Strategies for Antipsychotic-Related Sexual Dysfunction: A Clinical Approach.J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 15;10(2):308. doi: 10.3390/jcm10020308. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33467621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Case of Hyper Sexuality Probably Associated with Clozapine.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2018 Jun 20;48(4):20-24. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2018. PMID: 30618473 Free PMC article.
-
Management of common adverse effects of antipsychotic medications.World Psychiatry. 2018 Oct;17(3):341-356. doi: 10.1002/wps.20567. World Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30192094 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual dysfunction in patients with schizophrenia treated with conventional antipsychotics or risperidone.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2009;5:47-54. doi: 10.2147/ndt.s4766. Epub 2009 Apr 8. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2009. PMID: 19557099 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual dysfunction in Chinese rural patients with schizophrenia.BMC Psychiatry. 2019 Jul 12;19(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12888-019-2205-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31299942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duggan L, Fenton M, Dardennes RM, El-Dosoky A, Indran S. Olanzapine for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD001359–CD001359. - PubMed
-
- Waraich PS, Adams CE, Roque M, Hamill KM, Marti J. Haloperidol dose for the acute phase of schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(3):CD001951–CD001951. - PubMed
-
- Fenton M, Coutinho ES, Campbell C. Zuclopenthixol acetate in the treatment of acute schizophrenia and similar serious mental illnesses. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD000525–CD000525. - PubMed
-
- Bagnall A, Lewis RA, Leitner ML. Ziprasidone for schizophrenia and severe mental illness. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(4):CD001945–CD001945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical