Cryptococcus neoformans in organ transplant recipients: impact of calcineurin-inhibitor agents on mortality
- PMID: 17262720
- PMCID: PMC2746485
- DOI: 10.1086/511438
Cryptococcus neoformans in organ transplant recipients: impact of calcineurin-inhibitor agents on mortality
Abstract
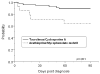
Variables influencing the risk of dissemination and outcome of Cryptococcus neoformans infection were assessed in 111 organ transplant recipients with cryptococcosis in a prospective, multicenter, international study. Sixty-one percent (68/111) of the patients had disseminated infection. The risk of disseminated cryptococcosis was significantly higher for liver transplant recipients (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 6.65; P=.048). The overall mortality rate at 90 days was 14% (16/111). The mortality rate was higher in patients with abnormal mental status (P=.023), renal failure at baseline (P=.028), fungemia (P=.006), and disseminated infection (P=.035) and was lower in those receiving a calcineurin-inhibitor agent (P=.003). In a multivariable analysis, the receipt of a calcineurin-inhibitor agent was independently associated with a lower mortality (adjusted HR, 0.21; P=.008), and renal failure at baseline with a higher mortality rate (adjusted HR, 3.14; P=.037). Thus, outcome in transplant recipients with cryptococcosis appears to be influenced by the type of immunosuppressive agent employed. Additionally, discerning the basis for transplant type-specific differences in disease severity has implications relevant for yielding further insights into the pathogenesis of C. neoformans infection in transplant recipients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kanj SS, Welty-Wolf K, Madden J, Tapson V, Baz MA, Davis D, Perfect JR. Fungal infections in lung and heart-lung transplant recipients: report of 9 cases and review of the literature. Medicine. 1996;75:142–156. - PubMed
-
- Paya CV. Fungal infections in solid-organ transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;16:677–688. - PubMed
-
- Fortun J, Martin-Davila P, Moreno S, Barcena R, de Vicente E, Honrubia A, Garcia M, Nuno J, Candela A, Uriarte M, Pintado V. Prevention of invasive fungal infections in liver transplant recipients: the role of prophylaxis with lipid formulations of amphotericin B in high-risk patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;52:813–819. - PubMed
-
- Singh N, Wagener MM, Marino IR, Gayowski T. Trends in invasive fungal infections in liver transplant recipients: correlation with evolution in transplantation practices. Transplantation. 2002;73:63–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

