Lack of indinavir-associated nephrological complications in HIV-infected adults (predominantly women) with high indinavir plasma concentration in Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire
- PMID: 17263634
- PMCID: PMC3219609
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2006.0038
Lack of indinavir-associated nephrological complications in HIV-infected adults (predominantly women) with high indinavir plasma concentration in Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire
Abstract
To report the tolerance of indinavir combined with ritonavir (IDV/r 800/100 mg) twice daily (bid) in sub-Saharan African HIV-infected adults. HAART-naives patients started zidovudine plus lamivudine plus IDV/r 800/100 mg bid. Follow-up included standardized documentation of morbidity, CD4(+) cell count, creatininemia, plasma HIV-1 RNA, and IDV minimal plasma concentration (C(min)) measurements at month 1 (M1), M3, and M6. Seventy HIV-1-infected adults (68 women, median CD4 235/mm(3)) started HAART. At M6, 63% had undetectable viral load, and the median gain in CD4 since baseline was +128/mm(3). During the first 6 months, 21 patients experimented with 23 treatment modifications (reduction in IDV/r 400/100 mg bid, n = 11; switch to efavirenz, n = 11; zidovudine replaced by stavudine, n = 1), including 22 for digestive intolerance and 1 for severe anemia. At M1, M3, and M6, 67, 59, and 48 patients were still receiving IDV/r 800/100 mg bid, of whom 70%, 72%, and 60% had IDV Cmin above 5 ng/ml, respectively. In these patients, at M1, M3, and M6, the mean (+/- SD) IDV C(min) were 3431 +/- 3835 ng/ml, 2288 +/- 2116 ng/ml, and 1543 +/- 2398 ng/ml, respectively. There was no renal insufficiency of any grade, and no symptoms of urinary stones. The IDV/r 800/100 mg bid-containing regimen led to high IDV Cmin and a high rate of digestive intolerance. There was a surprising lack of nephrological side effects during the 6 months of follow-up, supporting the hypothesis that nephrological tolerance of IDV might be higher in sub-Saharan African individuals than in Americans or Europeans.
Figures
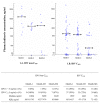
 : median value among patients with IDV concentration ≥ 10 ng/ml C: concentration; IQR: interquartile range
: median value among patients with IDV concentration ≥ 10 ng/ml C: concentration; IQR: interquartile rangeSimilar articles
-
Efficacy of a twice-daily antiretroviral regimen containing 100 mg ritonavir/400 mg indinavir in HIV-infected patients.AIDS. 2003 Jan 24;17(2):209-14. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200301240-00011. AIDS. 2003. PMID: 12545081 Clinical Trial.
-
[Efavirenz versus indinavir among HIV-1 naive patients in Abidjan (Ivory Coast)].Med Mal Infect. 2008 May;38(5):264-9. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2008.02.004. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Med Mal Infect. 2008. PMID: 18395375 French.
-
Determination of indinavir and nelfinavir trough plasma concentration efficacy thresholds according to virological response in HIV-infected patients.HIV Med. 2004 Jul;5(4):307-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1293.2004.00226.x. HIV Med. 2004. PMID: 15236622
-
Nephrotoxicity of antiretroviral therapy in an HIV-infected patient.Kidney Int. 2007 May;71(10):1071-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002134. Epub 2007 Feb 21. Kidney Int. 2007. PMID: 17311070 Review. No abstract available.
-
Symptomatic crystalluria associated with indinavir.Ann Pharmacother. 2000 Dec;34(12):1414-8. doi: 10.1345/aph.10092. Ann Pharmacother. 2000. PMID: 11144699 Review.
Cited by
-
Anthropometric and immunological success of antiretroviral therapy and prediction of virological success in west African adults.Bull World Health Organ. 2008 Jun;86(6):435-42. doi: 10.2471/blt.07.042911. Bull World Health Organ. 2008. PMID: 18568272 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Bucher HC, Bichsel M, Taffe P, et al. Ritonavir plus saquinavir versus single protease inhibitor therapy in protease inhibitor-naive HIV-infected patients: the Swiss HIV Cohort Study. HIV Med. 2002;3:247–53. - PubMed
-
- Aarnoutse RE, Wasmuth JC, Fatkenheuer G, et al. Administration of indinavir and low-dose ritonavir (800/100 mg twice daily) with food reduces nephrotoxic peak plasma levels of indinavir. Antivir Ther. 2003;8:309–14. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch MS, Brun-Vezinet F, Clotet B, et al. Antiretroviral drug resistance testing in adults infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1: 2003 recommendations of an International AIDS Society-USA Panel. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37:113–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

