Inhibition of HIV type 1 replication in CD4+ and CD14+ cells purified from HIV type 1-infected individuals by the 2-5A agonist immunomodulator, 2-5A(N6B)
- PMID: 17263642
- PMCID: PMC1941645
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2005.0091
Inhibition of HIV type 1 replication in CD4+ and CD14+ cells purified from HIV type 1-infected individuals by the 2-5A agonist immunomodulator, 2-5A(N6B)
Abstract
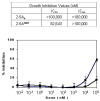
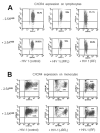
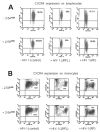
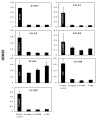
Two major interferon (IFN)-mediated antiviral defense enzymes are double-stranded (ds)RNA-dependent 2',5'-oligoadenylate (2-5A) synthetase (2-5OAS) and p68 kinase (PKR). When activated by dsRNA, 2-5OAS synthesizes 2-5A, which binds to and activates RNase L. Activated RNase L hydrolyzes single-stranded viral RNA, thereby inhibiting viral protein synthesis. HIV-1 inhibits the IFN-mediated intracellular antiviral pathways. We have reported the synthesis and characterization of a nuclease-resistant 2-5A agonist (2-5A(N6B)) that overcomes the HIV-1 induced blockades by restoring the 2-5OAS/RNase L antiviral pathway (Homan JW, et al., J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 2002;30:9-20). The objective of this study was to test the effect of 2-5A(N6B) on chronically infected CD4(+) T lymphocytes and CD14(+) monocytes derived from HIV-1-seropositive individuals. Wild-type HIV-1 replication was effectively inhibited by 2-5A(N6B) in CD4(+) T lymphocytes and CD14(+) monocytes purified from HIV-1 seropositive individuals (n = 18) compared to untreated cells. We also assessed the cytotoxicity of 2-5A(N6B) and report that 2-5A(N6B) exerts its anti-HIV-1 activity with no evidence of cytotoxicity (IC(90) > 100,000 nM). Furthermore, 2-5A(N6B) did not alter the cellular RNA profile, affect CCR5 or CXCR4 coreceptor expression, or activate caspase-dependent apoptosis. Evidence is also provided to show that 2-5A(N6B), and naturally occurring 2-5A(4), act as ligands to activate human Toll-like receptor 4. These results indicate that the 2-5A agonist 2-5A(N6B) has the potential to enhance host cell innate and acquired immune defense mechanisms against HIV-1 infection.
Figures


References
-
- Sen GC. Viruses and interferons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2001;55:255–281. - PubMed
-
- Goodbourn S, Didock L, Randall RE. Interferons: cell signaling, immune modulation, antiviral responses and virus countermeasures. J Gen Virol. 2000;81:2341–2364. - PubMed
-
- Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, et al. How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–264. - PubMed
-
- Dong B, Silverman RH. 2–5A-dependent RNase molecules dimerize during activation by 2- 5A. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:4133–4137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

