A gel-based proteomic comparison of human cerebrospinal fluid between inflicted and non-inflicted pediatric traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 17263669
- PMCID: PMC2721471
- DOI: 10.1089/neu.2006.0061
A gel-based proteomic comparison of human cerebrospinal fluid between inflicted and non-inflicted pediatric traumatic brain injury
Abstract
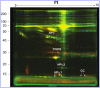
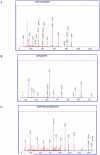
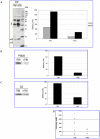
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is the most common cause of traumatic death in infancy, and inflicted TBI (iTBI) is the predominant cause. Like other central nervous system pathologies, TBI changes the composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which may represent a unique clinical window on brain pathophysiology. Proteomic analysis, including two-dimensional (2-D) difference in gel electrophoresis (DIGE) combined with mass spectrometry (MS), was used to compare the CSF protein profile of two pooled samples from pediatric iTBI (n = 13) and non-inflicted TBI (nTBI; n = 13) patients with severe injury. CSF proteins from iTBI and nTBI were fluorescently labeled in triplicate using different fluorescent Cy dyes and separated by 2-D gel electrophoresis. Approximately 250 protein spots were found in CSF, with 90% between-gel reproducibility of the 2-D gel. Following in-gel digestion, the tryptic peptides were analyzed by MS for protein identification. The acute phase reactant, haptoglobin (HP) isoforms, showed an approximate fourfold increase in nTBI versus iTBI. In contrast, the levels of prostaglandin D(2) synthase (PGDS) and cystatin C (CC) were 12-fold and sevenfold higher in iTBI versus nTBI, respectively. The changes of HP, PGDS, and CC were confirmed by Western blot. These initial results with conventional gel-based proteomics show new protein changes that may ultimately help to understand pathophysiological differences between iTBI and nTBI.
Figures
References
-
- ABRAHAMSON M, BARRETT AJ, SALVESEN G, GRUBB A. Isolation of six cysteine proteinase inhibitors from human urine. Their physicochemical and enzyme kinetic properties and concentrations in biological fluids. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:11282–11289. - PubMed
-
- ADELSON PD, KOCHANEK PM. Head injury in children. J. Child Neurol. 1998;13:2–15. - PubMed
-
- ALDRED AR, BRACK CM, SCHREIBER G. The cerebral expression of plasma protein genes in different species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995;111:1–15. - PubMed
-
- AMICK JE, YANDORA KA, BELL MJ, et al. The Th1 versus Th2 cytokine profile in cerebrospinal fluid after severe traumatic brain injury in infants and children. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2001;2:260–264. - PubMed
-
- BELL MJ, KOCHANEK PM, DOUGHTY LA, et al. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 in cerebrospinal fluid after severe traumatic brain injury in children. J. Neurotrauma. 1997;14:451–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS042648/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS030318/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD043843/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS 30318/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS030318/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD040686/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD 40686/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DA 021519/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- NS 42648/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DA021519/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- NS 38087/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS038087/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD 043843-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

