Statins synergistically potentiate 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) lethality in human leukemia and myeloma cells by disrupting Ras farnesylation and activation
- PMID: 17264303
- PMCID: PMC1885487
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-09-047076
Statins synergistically potentiate 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) lethality in human leukemia and myeloma cells by disrupting Ras farnesylation and activation
Abstract
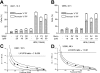
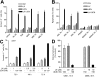
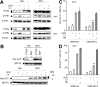
Interactions between UCN-01 and HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (ie, statins) have been examined in human leukemia and myeloma cells. Exposure of U937 and U266 cells to minimally toxic concentrations of UCN-01 and various statins (eg, lovastatin, simvastatin, or fluvastatin) dramatically increased mitochondrial dysfunction, caspase activation, and apoptosis. Comparable effects were observed in other leukemia and myeloma cell lines as well as in primary acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts but not in normal hematopoietic cells. Potentiation of UCN-01 lethality by lovastatin was associated with disruption of Ras prenylation and activation. These events were significantly attenuated by farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) but not by geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP), implicating perturbations in farnesylation rather than geranylgeranylation in synergistic interactions. Coexposure to statins and UCN-01 resulted in inactivation of ERK1/2 and Akt, accompanied by JNK activation. U266 cells ectopically expressing JNK1-APF, a dominant negative JNK1 mutant, displayed significantly reduced susceptibility to lovastatin/UCN-01-mediated lethality. Moreover, transfection of U266 cells with constitutively activated H-Ras (Q61L) attenuated ERK1/2 inactivation and dramatically diminished the lethality of this regimen. Collectively, these findings indicate that HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors act through a Ras farnesylation-associated mechanism to induce signaling perturbations, particularly prevention of Ras and ERK1/2 activation, in UCN-01-treated cells, resulting in the synergistic induction of cell death.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Farnesyltransferase inhibitors interact synergistically with the Chk1 inhibitor UCN-01 to induce apoptosis in human leukemia cells through interruption of both Akt and MEK/ERK pathways and activation of SEK1/JNK.Blood. 2005 Feb 15;105(4):1706-16. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-07-2767. Epub 2004 Oct 19. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15494423
-
Pharmacological inhibitors of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase/MAPK cascade interact synergistically with UCN-01 to induce mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in human leukemia cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Jul 1;61(13):5106-15. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11431348
-
Rapamycin and UCN-01 synergistically induce apoptosis in human leukemia cells through a process that is regulated by the Raf-1/MEK/ERK, Akt, and JNK signal transduction pathways.Mol Cancer Ther. 2005 Mar;4(3):457-70. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-04-0137. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005. PMID: 15767555
-
Synergistic antileukemic interactions between 17-AAG and UCN-01 involve interruption of RAF/MEK- and AKT-related pathways.Blood. 2003 Sep 1;102(5):1824-32. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3785. Epub 2003 May 8. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12738674
-
Targeting the Isoprenoid Biosynthetic Pathway in Multiple Myeloma.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;24(1):111. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010111. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled multi-centre phase III trial of XELIRI/FOLFIRI plus simvastatin for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.Br J Cancer. 2015 Nov 17;113(10):1421-6. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.371. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26505681 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
New insights into checkpoint kinase 1 in the DNA damage response signaling network.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jan 15;16(2):376-83. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1029. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20068082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Biological Effect of Non-UV-Activated Bergapten on Selected Human Tumor Cells and the Insight into the Molecular Mechanism of Its Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 25;24(21):15555. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115555. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958539 Free PMC article.
-
Statins Perturb Gβγ Signaling and Cell Behavior in a Gγ Subtype Dependent Manner.Mol Pharmacol. 2019 Apr;95(4):361-375. doi: 10.1124/mol.118.114710. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Mol Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30765461 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin regulates the proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion of human acute myeloid leukemia cells via miR-19a-3p/HIF-1α axis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):11898-11908. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1999552. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34895042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tobert JA. Lovastatin and beyond: the history of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:517–526. - PubMed
-
- Graaf MR, Richel DJ, van Noorden CJ, Guchelaar HJ. Effects of statins and farnesyltransferase inhibitors on the development and progression of cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2004;30:609–641. - PubMed
-
- Swanson KM, Hohl RJ. Anti-cancer therapy: targeting the mevalonate pathway. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2006;6:15–37. - PubMed
-
- Downward J. Targeting RAS signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:11–22. - PubMed
-
- Reuter CW, Morgan MA, Bergmann L. Targeting the Ras signaling pathway: a rational, mechanism-based treatment for hematologic malignancies? Blood. 2000;96:1655–1669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

