Characterization of an Oct1 orthologue in the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus: a negative regulator of immunoglobulin gene transcription?
- PMID: 17266766
- PMCID: PMC1800861
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-8
Characterization of an Oct1 orthologue in the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus: a negative regulator of immunoglobulin gene transcription?
Abstract
Background: The enhancer (Emu3') of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus (IGH) of the channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) has been well characterized. The functional core region consists of two variant Oct transcription factor binding octamer motifs and one E-protein binding muE5 site. An orthologue to the Oct2 transcription factor has previously been cloned in catfish and is a functionally active transcription factor. This study was undertaken to clone and characterize the Oct1 transcription factor, which has also been shown to be important in driving immunoglobulin gene transcription in mammals.
Results: An orthologue of Oct1, a POU family transcription factor, was cloned from a catfish macrophage cDNA library. The inferred amino acid sequence of the catfish Oct1, when aligned with other vertebrate Oct1 sequences, revealed clear conservation of structure, with the POU specific subdomain of catfish Oct1 showing 96% identity to that of mouse Oct1. Expression of Oct1 was observed in clonal T and B cell lines and in all tissues examined. Catfish Oct1, when transfected into both mammalian (mouse) and catfish B cell lines, unexpectedly failed to drive transcription from three different octamer-containing reporter constructs. These contained a trimer of octamer motifs, a fish VH promoter, and the core region of the catfish Emu3' IGH enhancer, respectively. This failure of catfish Oct1 to drive transcription was not rescued by human BOB.1, a co-activator of Oct transcription factors that stimulates transcription driven by catfish Oct2. When co-transfected with catfish Oct2, Oct1 reduced Oct2 driven transcriptional activation. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays showed that catfish Oct1 (native or expressed in vitro) bound both consensus and variant octamer motifs. Putative N- and C-terminal activation domains of Oct1, when fused to a Gal4 DNA binding domain and co-transfected with Gal4-dependent reporter constructs were transcriptionally inactive, which may be due in part to a lack of residues associated with activation domain function.
Conclusion: An orthologue to mammalian Oct1 has been found in the catfish. It is similar to mammalian Oct1 in structure and expression. However, these results indicate that the physiological functions of catfish Oct1 differ from those of mammalian Oct1 and include negative regulation of transcription.
Figures
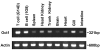





Similar articles
-
BOB.1 of the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus: not a transcriptional coactivator?Mol Immunol. 2009 Jan;46(3):481-91. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19041136 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Oct2 from the channel catfish: functional preference for a variant octamer motif.J Immunol. 1998 Apr 15;160(8):3874-82. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9558093
-
Regulation of immunoglobulin gene transcription in a teleost fish: identification, expression and functional properties of E2A in the channel catfish.Immunogenetics. 2005 May;57(3-4):273-82. doi: 10.1007/s00251-005-0793-3. Epub 2005 Apr 8. Immunogenetics. 2005. PMID: 15900499 Free PMC article.
-
Octamer-binding transcription factors: genomics and functions.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013 Jun 1;18(3):1051-71. doi: 10.2741/4162. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013. PMID: 23747866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oct1 transcription factor and epithelial malignancies: Old protein learns new tricks.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jun;1859(6):792-804. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.02.007. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26877236 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
BOB.1 of the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus: not a transcriptional coactivator?Mol Immunol. 2009 Jan;46(3):481-91. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19041136 Free PMC article.
-
The zebrafish IgH locus contains multiple transcriptional regulatory regions.Dev Comp Immunol. 2011 Mar;35(3):352-9. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2010.10.010. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Dev Comp Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21055416 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated OCT1 participates in colon tumorigenesis and independently predicts poor prognoses of colorectal cancer patients.Tumour Biol. 2016 Mar;37(3):3247-55. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4080-0. Epub 2015 Oct 4. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26433389 Free PMC article.
-
Function of E-protein dimers expressed in catfish lymphocytes.Mol Immunol. 2008 Feb;45(4):1165-70. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.08.001. Epub 2007 Sep 17. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 17870169 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between E-protein and Oct transcription factors in the function of the catfish IGH enhancer.Dev Comp Immunol. 2008;32(10):1105-10. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.04.001. Epub 2008 May 7. Dev Comp Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18511119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- LaBella F, Sive HL, Roeder RG, Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988;2:32–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

