Changes in gene expression during pegylated interferon and ribavirin therapy of chronic hepatitis C virus distinguish responders from nonresponders to antiviral therapy
- PMID: 17267482
- PMCID: PMC1866036
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02640-06
Changes in gene expression during pegylated interferon and ribavirin therapy of chronic hepatitis C virus distinguish responders from nonresponders to antiviral therapy
Abstract
Treating chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection using pegylated alpha interferon and ribavirin leads to sustained clearance of virus and clinical improvement in approximately 50% of patients. Response rates are lower among patients with genotype 1 than with genotypes 2 and 3 and among African-American (AA) patients compared to Caucasian (CA) patients. Using DNA microarrays, gene expression was assessed for a group of 33 African-American and 36 Caucasian American patients with chronic HCV genotype 1 infection during the first 28 days of treatment. Results were examined with respect to treatment responses and to race. Patients showed a response to treatment at the gene expression level in RNA isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells irrespective of degree of decrease in HCV RNA levels. However, gene expression responses were relatively blunted in patients with poor viral response (<1.5 log(10)-IU/ml decrease at 28 days) compared to those in patients with a marked (>3.5 log(10)-IU/ml decrease) or intermediate (1.5 to 3.5 log(10)-IU/ml decrease) response. The number of genes that were up- or down-regulated by pegylated interferon and ribavirin treatment was fewer in patients with a poor response than in those with an intermediate or marked viral response. However AA patients had a stronger interferon response than CA patients in general. The induced levels of known interferon-stimulated genes such as the 2'5'-oligoadenylate synthetase, MX1, IRF-7, and toll-like receptor TLR-7 genes was lower in poor-response patients than in marked- or intermediate-response patients. Thus, the relative lack of viral response to interferon therapy of hepatitis C virus infection is associated with blunted interferon cell signaling. No specific regulatory gene could be identified as responsible for this global blunting or the racial differences.
Figures
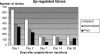

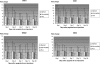
References
-
- Armstrong, G. L., A. Wasley, E. P. Simard, G. M. McQuillan, W. L. Kuhnert, and M. J. Alter. 2005. The prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in the United States, 1999 through 2002. Ann. Intern. Med. 144:705-714. - PubMed
-
- Cassatella, M. A., S. Gasperini, F. Calzetti, A. Bertagnin, A. D. Luster, and P. P. McDonald. 1997. Regulated production of the interferon-gamma-inducible protein-10 (IP-10) chemokine by human neutrophils. Eur. J. Immunol. 27:111-115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- U01 DK 60309/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060345/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60342/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000645/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000046/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR 00046/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60346/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60329/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60340/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60327/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK066144/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR 16500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR 000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060327/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060349/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060342/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060352/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016500/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M02 RR 000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR 000645/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60345/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060335/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60352/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060309/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60349/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000042/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060344/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060346/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060340/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60335/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60344/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK 60341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK060329/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK 066144/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

