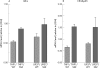Sulfasalazine sensitises human monocytic/macrophage cells for glucocorticoids by upregulation of glucocorticoid receptor alpha and glucocorticoid induced apoptosis
- PMID: 17267514
- PMCID: PMC1994309
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.060509
Sulfasalazine sensitises human monocytic/macrophage cells for glucocorticoids by upregulation of glucocorticoid receptor alpha and glucocorticoid induced apoptosis
Abstract
Background: Glucocorticoids (GCs) are commonly used in the treatment of (chronic) inflammatory diseases and cancer, but inherent or acquired resistance to these drugs limits their optimal efficacy. The availability of drugs that could modulate GC resistance is therefore of potential clinical interest.
Objective: To explore the molecular basis of GC sensitisation of GC resistant monocytic/macrophage cells after chronic exposure to sulfasalazine.
Methods: Human monocytic/macrophage THP1 and U937 cells represent a cell line model system characterised by inherent resistance to the GCs dexamethasone and prednisolone. Both cell lines were chronically exposed in vitro to 0.3-0.6 mM sulfasalazine (SSZ) for approximately 3 months, after which they were characterised for GC sensitivity, expression levels of GC receptor and components of the nuclear factor kappa B (NFkappaB) signalling pathway, and their ability to undergo GC induced apoptosis.
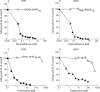
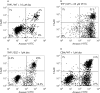
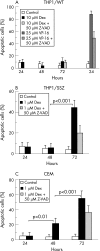
Results: Chronic exposure to SSZ markedly sensitised both U937 and THP1 cells to dexamethasone (781-fold and 1389-fold, respectively) and prednisolone (562-fold and 1220-fold, respectively). Restoration of GC sensitivity in cells exposed to SSZ was provoked via GC induced apoptosis, coinciding with inhibition of NFkappaB activation. Moreover, western blot analysis revealed a markedly increased expression of glucocorticoid receptor alpha (GRalpha) in cells exposed to SSZ. Since GRalpha mRNA levels were only marginally increased, these results suggest that an altered post-transcriptional mechanism was operable which conferred a stable GRalpha protein on SSZ exposed cells.
Conclusion: These results suggest that chronic targeting of the NFkappaB signalling pathway by SSZ may be exploited as a novel strategy to stabilise GRalpha expression and thereby sensitise primary resistant cells to GCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoid receptor alpha isoform-selective regulation of antiapoptotic genes in osteosarcoma cells: a new mechanism for glucocorticoid resistance.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Jul;25(7):1087-99. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0051. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21527497 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin sensitizes glucocorticoid resistant acute lymphoblastic leukemia CEM-C1 cells to dexamethasone induced apoptosis through both mTOR suppression and up-regulation and activation of glucocorticoid receptor.Biomed Environ Sci. 2013 May;26(5):371-81. doi: 10.3967/0895-3988.2013.05.006. Biomed Environ Sci. 2013. PMID: 23611130
-
Sulfasalazine down-regulates the expression of the angiogenic factors platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor/thymidine phosphorylase and interleukin-8 in human monocytic-macrophage THP1 and U937 cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Oct;66(4):1054-60. doi: 10.1124/mol.104.000315. Epub 2004 Jul 21. Mol Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15269287
-
Acquired Glucocorticoid Resistance Due to Homologous Glucocorticoid Receptor Downregulation: A Modern Look at an Age-Old Problem.Cells. 2021 Sep 24;10(10):2529. doi: 10.3390/cells10102529. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid modulation of human monocyte/macrophage function: control of TNF-alpha secretion.Inflamm Res. 1997 Nov;46(11):447-51. doi: 10.1007/s000110050222. Inflamm Res. 1997. PMID: 9427064 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of reactive oxygen species in inflammation and cancer.MedComm (2020). 2024 Apr 4;5(4):e519. doi: 10.1002/mco2.519. eCollection 2024 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38576456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Modulation as Adjunctive Therapy for Pneumocystis pneumonia.Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2011;2011:918038. doi: 10.1155/2011/918038. Epub 2011 Aug 29. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21904545 Free PMC article.
-
Signals and Mechanisms Regulating Monocyte and Macrophage Activation in the Pathogenesis of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 26;22(15):7960. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157960. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression profiling of leukemic cells and primary thymocytes predicts a signature for apoptotic sensitivity to glucocorticoids.Cancer Cell Int. 2007 Nov 28;7:18. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-7-18. Cancer Cell Int. 2007. PMID: 18045478 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of the IGF2-mRNA binding protein p62 in transgenic mice induces a steatotic phenotype.J Hepatol. 2011 May;54(5):994-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.08.034. Epub 2010 Oct 26. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21145819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buttgereit F, Straub R H, Wehling M, Burmester G R. Glucocorticoids in the treatment of rheumatic diseases: an update on the mechanisms of action. Arthritis Rheum 2004503408–3417. - PubMed
-
- Greenstein S, Ghias K, Krett N L, Rosen S T. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid‐mediated apoptosis in hematological malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 200281681–1694. - PubMed
-
- Kaspers G J, Veerman A J. Clinical significance of cellular drug resistance in childhood leukemia. Recent Results Cancer Res 2003161196–220. - PubMed
-
- McKay L I, Cidlowski J A. Molecular control of immune/inflammatory responses: interactions between nuclear factor‐kappa B and steroid receptor‐signaling pathways. Endocr Rev 199920435–459. - PubMed
-
- De Bosscher K, Vanden Berghe W, Haegeman G. The interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor‐kappaB or activator protein‐1: molecular mechanisms for gene repression. Endocr Rev 200324488–522. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous