P2Y1 receptor modulation of the pre-Bötzinger complex inspiratory rhythm generating network in vitro
- PMID: 17267553
- PMCID: PMC6673186
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3948-06.2007
P2Y1 receptor modulation of the pre-Bötzinger complex inspiratory rhythm generating network in vitro
Abstract
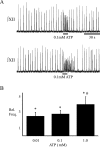
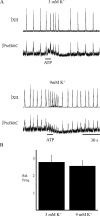
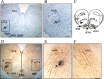
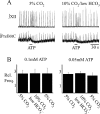
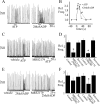
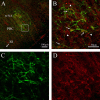
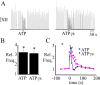
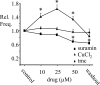
ATP is released during hypoxia from the ventrolateral medulla (VLM) and activates purinergic P2 receptors (P2Rs) at unknown loci to offset the secondary hypoxic depression of breathing. In this study, we used rhythmically active medullary slices from neonatal rat to map, in relation to anatomical and molecular markers of the pre-Bötzinger complex (preBötC) (a proposed site of rhythm generation), the effects of ATP on respiratory rhythm and identify the P2R subtypes responsible for these actions. Unilateral microinjections of ATP in a three-dimensional grid within the VLM revealed a "hotspot" where ATP (0.1 mM) evoked a rapid 2.2 +/- 0.1-fold increase in inspiratory frequency followed by a brief reduction to 0.83 +/- 0.02 of baseline. The hotspot was identified as the preBötC based on histology, overlap of injection sites with NK1R immunolabeling, and potentiation or inhibition of respiratory frequency by SP ([Sar9-Met(O2)11]-substance P) or DAMGO ([D-Ala2,N-MePhe4,Gly-ol5]-enkephalin), respectively. The relative potency of P2R agonists [2MeSADP (2-methylthioadenosine 5'-diphosphate) approximately = 2MeSATP (2-methylthioadenosine 5'-triphosphate) approximately = ATPgammas (adenosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate tetralithium salt) approximately = ATP >> UTP approximately = alphabeta meATP (alpha,beta-methylene-adenosine 5'-triphosphate)] and attenuation of the ATP response by MRS2179 (2'-deoxy-N6-methyladenosine-3',5'-bisphosphate) (P2Y1 antagonist) indicate that the excitation is mediated by P2Y1Rs. The post-ATP inhibition, which was never observed in response to ATPgammas, is dependent on ATP hydrolysis. These data establish in neonatal rats that respiratory rhythm generating networks in the preBötC are exquisitely sensitive to P2Y1R activation, and suggest a role for P2Y1Rs in respiratory motor control, particularly in the P2R excitation of rhythm that occurs during hypoxia.
Figures




References
-
- Brosenitsch TA, Adachi T, Lipski J, Housley GD, Funk GD. Developmental downregulation of P2X3 receptors in motoneurons of the compact formation of the nucleus ambiguus. Eur J Neurosci. 2005;22:809–824. - PubMed
-
- Dale N, Gilday D. Regulation of rhythmic movements by purinergic neurotransmitters in frog embryos. Nature. 1996;383:259–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
