Endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor triggers fast calcium transients at synapses in developing dendrites
- PMID: 17267564
- PMCID: PMC6673203
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3590-06.2007
Endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor triggers fast calcium transients at synapses in developing dendrites
Abstract
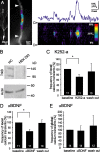
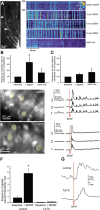
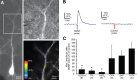
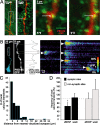
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is involved in many aspects of the formation of functional neuronal networks. BDNF signaling regulates neuronal development not only globally, at the level of entire neurons or networks, but also at a subcellular level and with high temporal specificity; however, the spatiotemporal characteristics of intrinsic BDNF signaling are essentially unknown. Here, we used calcium imaging to directly observe intrinsic BDNF signaling in developing hippocampal neurons. We found that blocking intrinsic BDNF signaling with function-blocking BDNF antibodies (alphaBDNF) or K252-a reduced the frequency of spontaneously occurring fast and localized calcium rises in dendrites. Conversely, focal application of BDNF evoked fast and local dendritic calcium transients, which required activation of TrkB (tropomyosin-related kinase B) receptors as well as activation of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels. Virus-mediated expression of PSD-95:CFP (postsynaptic density-95 tagged with cyan fluorescent protein) revealed that spontaneous local calcium transients occurred frequently at postsynaptic sites along the dendrite. The frequency of synaptically localized calcium transients was specifically reduced by blocking intrinsic BDNF signaling, whereas nonsynaptic calcium rises were not affected. Furthermore, focal BDNF delivery evoked localized and fast calcium elevations specifically at postsynaptic sites. Together, our results demonstrate that BDNF-dependent calcium signaling in developing hippocampal neurons is fast and occurs at synapses. These temporal and spatial characteristics of intrinsic BDNF signaling as well as its relative abundance renders BDNF an ideal signaling molecule in the establishment of specific synaptic connectivity and functional neuronal networks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postsynaptic secretion of BDNF and NT-3 from hippocampal neurons depends on calcium calmodulin kinase II signaling and proceeds via delayed fusion pore opening.J Neurosci. 2007 Sep 26;27(39):10350-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0692-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17898207 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of neuronal calcium signaling by neurotrophic factors.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2002 Jun-Aug;20(3-5):199-207. doi: 10.1016/s0736-5748(02)00014-x. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12175855 Free PMC article.
-
Altered balance of glutamatergic/GABAergic synaptic input and associated changes in dendrite morphology after BDNF expression in BDNF-deficient hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2006 Jul 5;26(27):7189-200. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5474-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16822976 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF mechanisms in late LTP formation: A synthesis and breakdown.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:664-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.06.024. Epub 2013 Jul 2. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23831365 Review.
-
A common thread for pain and memory synapses? Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and trkB receptors.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003 Mar;24(3):116-21. doi: 10.1016/S0165-6147(03)00025-7. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003. PMID: 12628355 Review.
Cited by
-
Remodelling of the respiratory network in a mouse model of Rett syndrome depends on brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulated slow calcium buffering.J Physiol. 2009 Jun 1;587(Pt 11):2473-85. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.169805. Epub 2009 Apr 9. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19359374 Free PMC article.
-
The role of neurotrophic factors in novel, rapid psychiatric treatments.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Jan;49(1):227-245. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01717-x. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 37673965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Xuefu Zhuyu decoction improves neurological dysfunction by increasing synapsin expression after traumatic brain injury.Neural Regen Res. 2018 Aug;13(8):1417-1424. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.235297. Neural Regen Res. 2018. PMID: 30106054 Free PMC article.
-
Stepping Out of the Shade: Control of Neuronal Activity by the Scaffold Protein Kidins220/ARMS.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Mar 14;10:68. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00068. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27013979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acupuncture Improved Neurological Recovery after Traumatic Brain Injury by Activating BDNF/TrkB Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:8460145. doi: 10.1155/2017/8460145. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28243312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berninger B, Garcia DE, Inagaki N, Hahnel C, Lindholm D. BDNF and NT-3 induce intracellular Ca 2+ elevation in hippocampal neurones. NeuroReport. 1993;4:1303–1306. - PubMed
-
- Bibel M, Barde YA. Neurotrophins: key regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous system. Genes Dev. 2000;14:2919–2937. - PubMed
-
- Blum R, Kafitz KW, Konnerth A. Neurotrophin-evoked depolarization requires the sodium channel Na(V)1.9. Nature. 2002;419:687–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
