Transducin translocation in rods is triggered by saturation of the GTPase-activating complex
- PMID: 17267570
- PMCID: PMC6673185
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5010-06.2007
Transducin translocation in rods is triggered by saturation of the GTPase-activating complex
Abstract
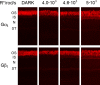
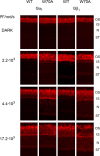
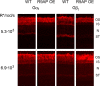
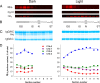
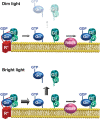
Light causes massive translocation of G-protein transducin from the light-sensitive outer segment compartment of the rod photoreceptor cell. Remarkably, significant translocation is observed only when the light intensity exceeds a critical threshold level. We addressed the nature of this threshold using a series of mutant mice and found that the threshold can be shifted to either a lower or higher light intensity, dependent on whether the ability of the GTPase-activating complex to inactivate GTP-bound transducin is decreased or increased. We also demonstrated that the threshold is not dependent on cellular signaling downstream from transducin. Finally, we showed that the extent of transducin alpha subunit translocation is affected by the hydrophobicity of its acyl modification. This implies that interactions with membranes impose a limitation on transducin translocation. Our data suggest that transducin translocation is triggered when the cell exhausts its capacity to activate transducin GTPase, and a portion of transducin remains active for a sufficient time to dissociate from membranes and to escape from the outer segment. Overall, the threshold marks the switch of the rod from the highly light-sensitive mode of operation required under limited lighting conditions to the less-sensitive energy-saving mode beneficial in bright light, when vision is dominated by cones.
Figures

Comment in
-
Transducin in rod photoreceptors: translocated when not terminated.J Neurosci. 2007 Jun 13;27(24):6349-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1399-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17567795 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Angleson JK, Wensel TG. Enhancement of rod outer segment GTPase accelerating protein activity by the inhibitory subunit of cGMP phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:16290–16296. - PubMed
-
- Arshavsky VY, Dumke CL, Zhu Y, Artemyev NO, Skiba NP, Hamm HE, Bownds MD. Regulation of transducin GTPase activity in bovine rod outer segments. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:19882–19887. - PubMed
-
- Brann MR, Cohen LV. Diurnal expression of transducin mRNA and translocation of transducin in rods of rat retina. Science. 1987;235:585–587. - PubMed
-
- Burns ME, Arshavsky VY. Beyond counting photons: trials and trends in vertebrate visual transduction. Neuron. 2005;48:387–401. - PubMed
-
- Calvert PD, Strissel KJ, Schiesser WE, Pugh EN, Jr, Arshavsky VY. Light-driven translocation of signaling proteins in vertebrate photoreceptors. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:560–568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
