Presynaptic monoacylglycerol lipase activity determines basal endocannabinoid tone and terminates retrograde endocannabinoid signaling in the hippocampus
- PMID: 17267577
- PMCID: PMC6673197
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4159-06.2007
Presynaptic monoacylglycerol lipase activity determines basal endocannabinoid tone and terminates retrograde endocannabinoid signaling in the hippocampus
Abstract
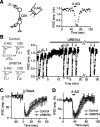
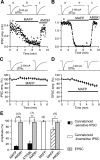
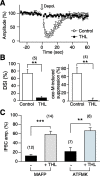
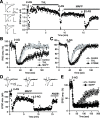
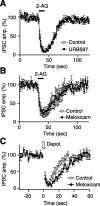
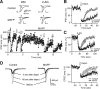
Endocannabinoids function as retrograde messengers and modulate synaptic transmission through presynaptic cannabinoid CB1 receptors. The magnitude and time course of endocannabinoid signaling are thought to depend on the balance between the production and degradation of endocannabinoids. The major endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) is hydrolyzed by monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL), which is shown to be localized at axon terminals. In the present study, we investigated how MGL regulates endocannabinoid signaling and influences synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. We found that MGL inhibitors, methyl arachidonoyl fluorophosphonate and arachidonoyl trifluoromethylketone, caused a gradual suppression of cannabinoid-sensitive IPSCs in cultured hippocampal neurons. This suppression was reversed by blocking CB1 receptors and was attenuated by inhibiting 2-AG synthesis, indicating that MGL scavenges constitutively released 2-AG. We also found that the MGL inhibitors significantly prolonged the suppression of both IPSCs and EPSCs induced by exogenous 2-AG and depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition/excitation, a phenomenon known to be mediated by retrograde endocannabinoid signaling. In contrast, inhibitors of other endocannabinoid hydrolyzing enzymes, fatty acid amide hydrolase and cyclooxygenase-2, had no effect on the 2-AG-induced IPSC suppression. These results strongly suggest that presynaptic MGL not only hydrolyzes 2-AG released from activated postsynaptic neurons but also contributes to degradation of constitutively produced 2-AG and prevention of its accumulation around presynaptic terminals. Thus, the MGL activity determines basal endocannabinoid tone and terminates retrograde endocannabinoid signaling in the hippocampus.
Figures

References
-
- Alger BE. Retrograde signaling in the regulation of synaptic transmission: focus on endocannabinoids. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;68:247–286. - PubMed
-
- Bisogno T, Howell F, Williams G, Minassi A, Cascio MG, Ligresti A, Matias I, Schiano-Moriello A, Paul P, Williams EJ, Gangadharan U, Hobbs C, Di Marzo V, Doherty P. Cloning of the first sn1-DAG lipases points to the spatial and temporal regulation of endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. J Cell Biol. 2003;163:463–468. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chevaleyre V, Castillo PE. Heterosynaptic LTD of hippocampal GABAergic synapses: a novel role of endocannabinoids in regulating excitability. Neuron. 2003;38:461–472. - PubMed
-
- Chevaleyre V, Takahashi KA, Castillo PE. Endocannabinoid-mediated synaptic plasticity in the CNS. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2006;29:37–76. - PubMed
-
- Cravatt BF, Giang DK, Mayfield SP, Boger DL, Lerner RA, Gilula NB. Molecular characterization of an enzyme that degrades neuromodulatory fatty-acid amides. Nature. 1996;384:83–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
