Cellular immunity in adolescents and adults following acellular pertussis vaccine administration
- PMID: 17267589
- PMCID: PMC1828844
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00364-06
Cellular immunity in adolescents and adults following acellular pertussis vaccine administration
Abstract
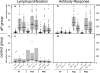
Cell-mediated immune (CMI) responses to an acellular pertussis vaccine administered to 49 subjects, a subset of participants in the National Institutes of Health-funded adult acellular pertussis vaccine efficacy trial, were evaluated and compared with antibody responses to vaccine antigens. Levels of proliferation of and cytokine secretion from lymphocytes cultured in the presence of pertussis toxin, filamentous hemagglutinin, or pertactin were measured before vaccination and 1 month and 1 year after vaccination. Statistically significant increases in lymphocyte stimulation indices and cytokine secretion were noted at both 1 month and 1 year after vaccination. Brisk pertussis antigen-specific immunoglobulin G responses were also noted at 1 month after vaccination, but these responses had declined by nearly 50% at 1 year after vaccination. These studies clearly demonstrate that both cellular and humoral immune responses occur after the administration of acellular pertussis vaccines to adolescents and adults but that the CMI responses are of greater magnitude and longer duration. CMI responses may be a better correlate of long-term protection.
Figures
References
-
- Ausiello, C. M., R. Lande, A. la Sala, F. Urbani, and A. Cassone. 1998. Cell-mediated immune response of healthy adults to Bordetella pertussis vaccine antigens. J. Infect. Dis. 178:466-470. - PubMed
-
- Ausiello, C. M., R. Lande, F. Urbani, B. Di Carlo, P. Stefanelli, S. Salmaso, P. Mastrantonio, and A. Cassone. 2000. Cell-mediated immunity and antibody responses to Bordetella pertussis antigens in children with a history of pertussis infection and in recipients of an acellular pertussis vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 181:1989-1995. - PubMed
-
- Cassone, A., P. Mastrantonio, and C. M. Ausiello. 2000. Are only antibody levels involved in the protection against pertussis in acellular pertussis vaccine recipients? J. Infect. Dis. 182:1575-1577. - PubMed
-
- Cherry, J. D., S. J. Chang, D. Klein, M. Lee, S. Barenkamp, D. Bernstein, R. Edelman, M. D. Decker, D. P. Greenberg, W. Keitel, J. Treanor, and J. I. Ward. 2004. Prevalence of antibody to Bordetella pertussis antigens in serum specimens obtained from 1793 adolescents and adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 39:1715-1718. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

